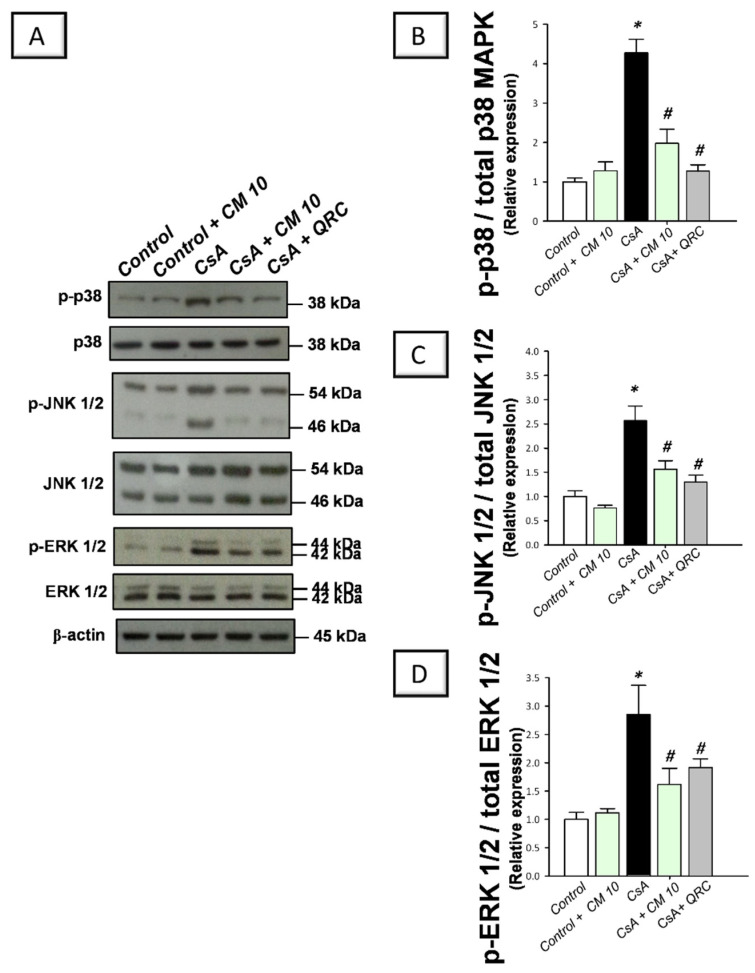
Figure 5.
Effect of camel milk administration on the transduction of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in cyclosporine-evoked renal damage in rats. (A) Representative immuno-blots that demonstrate the suppression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by camel milk, as evidenced by lowered expression of phospho-p38 (p-p38) MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182)/total p38 MAPK, phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/2 (p-JNK1/2 (Thr 183/185)/total JNK1/2, and phospho- extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204)/total ERK1/2 ratios. (B) Band intensity quantification of p38MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182)/total p38 MAPK relative protein expression. (C) Band intensity quantification of p-JNK1/2 (Thr 183/185)/total JNK1/2 relative protein expression. (D) Band intensity quantification of p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204)/total ERK1/2 relative protein expression. Values for the Western blotting are displayed as mean ± SEM, for n = 3 independent experiments per each group. The X-ray films were photographed with an HD-Nikon camera and the densitometric analysis of protein bands was carried out using Image J software. Equal loading/protein transfer was proven by probing with anti-β-actin. * Significance vs. control values at p < 0.05; # Significance vs. CsA values at p < 0.05. CsA, cyclosporine (20 mg/kg/day, s.c., for 3 weeks); CM 10, camel milk (10 mL/kg/day, by gavage, for 3 weeks); QRC; the reference antioxidant quercetin (50 mg/kg/day, by gavage, for 3 weeks). Original western blot images are shown in Figure S2.