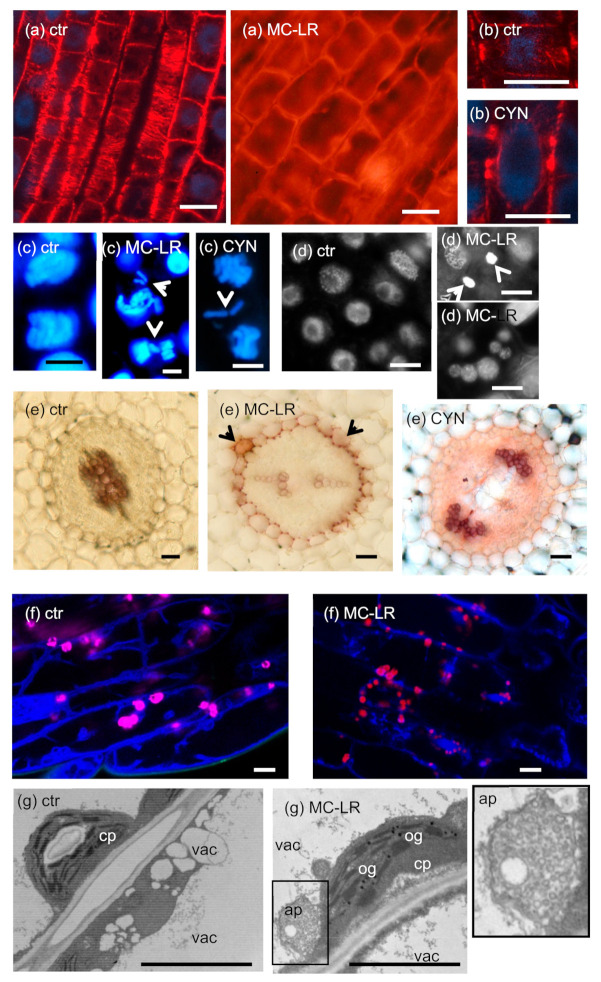
Figure 2.
Characteristic subcellular alterations induced by MC-LR and CYN. Panels (a–c) etc. refer to distinct subcellular features; toxin treatments are presented alongside with controls (ctr). (a) Phragmites australis roots, control cells present normal cortical microtubules (CMTs), while two day-treatments with 20 µM MC-LR induce depolymerization of CMTs and radial swelling of cells. (b) 10 µM CYN induces the formation of double preprophase bands (PPBs) in P. australis roots. (c) Long-term treatments with high (≥5 µM) concentrations of both MC-LR and CYN induce the formation of lagging chromosomes during cytokinesis and in general, mis-segregation of sister chromatids (arrowheads) in roots of Vicia faba. (d) 40 µM MC-LR induces chromatin condensation in roots of P. australis (upper image), and 10 µM MC-LR induces the formation of numerous nuclear fragments in roots of V. faba. Control nuclei are from roots of P. australis. (e) Phloroglucinol-HCl labels lignin purple. Only walls of xylem cells are labeled in control Sinapis alba roots, while 5 µM MC-LR induces uniform labeling of endodermal cell walls (arrowheads), and 10 µM CYN induces cell wall lignification in the whole stele. The inhibition of xylem differentiation by MC-LR and cell swelling in pith tissue by CYN are noteworthy. (f) Vacuolar systems of young Arabidopsis hypocotyl cells shown by tonoplast labeling with the fluorescent dye CACAIN and chloroplast autofluorescence (pink pseudo-coloring). Controls show vacuoles of different sizes, while 4-h treatment with 5 µM MC-LR induces strong fragmentation of vacuoles. (g) TEM images of young Arabidopsis hypocotyl cells. 24-h treatment with 2 µM MC-LR induces the formation of osmiophilic granules (og) in chloroplasts (cp) and the formation of autophagosome-like structures (ap). This latter structure is boxed and shown in detail (image on the right) to show its double-membrane envelope and many membrane vesicles inside. vac-vacuole. Scalebars: 50 µm (a,e), 10 µm (b,d,f), 5 µm (c,g). Microscopic images collected by L. Székvölgyi (a/ctr), J. Roszik (b), C. Máthé (a/MC-LR, c,d), M. M-Hamvas (e), Gy. Vereb (f), and K. Bóka (g). These micrographs were not published previously, and all authors agreed to their publication here.