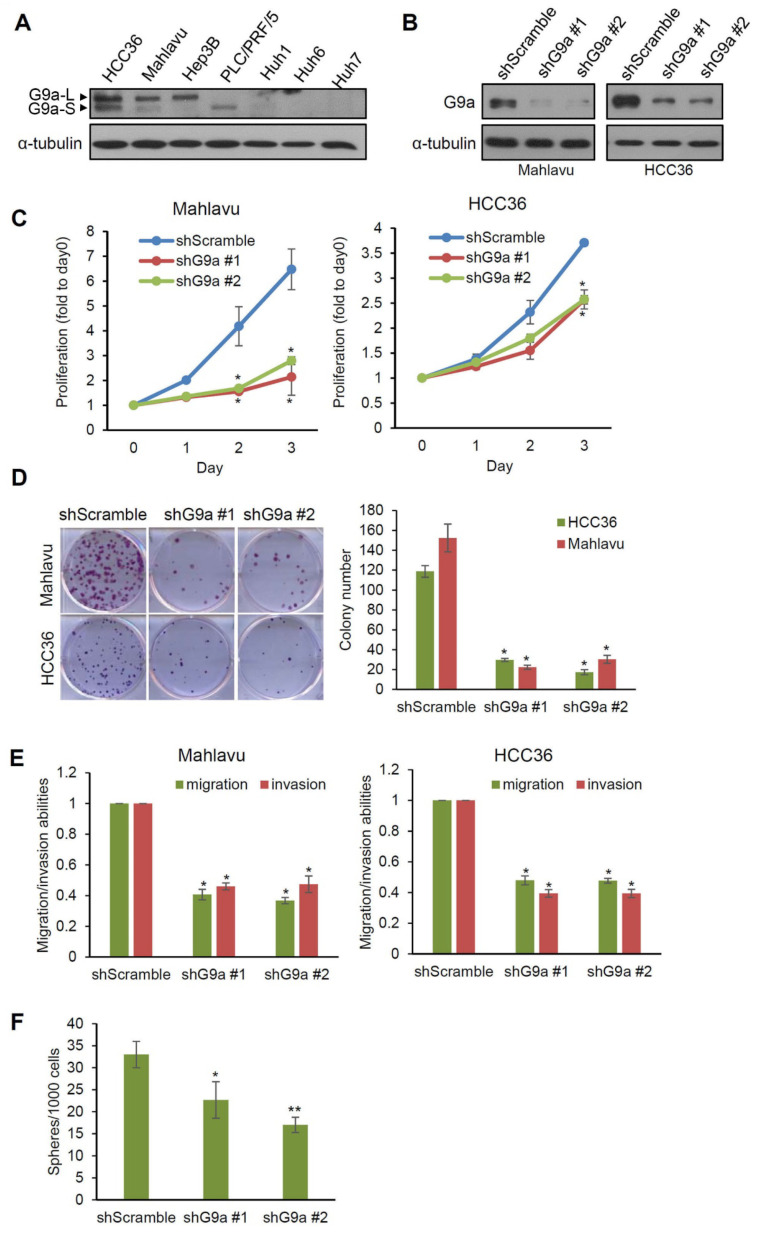
Figure 2.
G9a is associated with aggressive phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. (A) G9a protein expression levels of seven HCC cell lines were determined by immunoblotting. The short form (G9a-S, 160 KDa) or long form (G9a-L, 180 KDa) of G9a can be detected in these cells and are indicated by arrows. (B) Knockdown efficiencies of two G9a-specific shRNAs were examined by immunoblotting in Mahlavu and HCC36 HCC cells. (C) Three-day proliferation curves were determined in Mahlavu and HCC36 cells with either G9a shRNAs or control shRNA expressions by an MTT assay. Proliferation rates were significantly lower in cells stably transfected with G9a shRNA compared to control cells. (D) The clonogenic cell survival assay and the quantification results of Mahlavu and HCC36 cells with control or G9a shRNA expressions. All values are the means of three independent experiments. (E) Transwell migration and invasion assays of G9a knockdown in Mahlavu and HCC36 cells. Quantitative plot showing multiples of the control. (F) Sphere-forming ability of Mahlavu cells with control or G9a shRNA expression after 2 weeks of inoculation. Three independent replicates were performed in each experiment. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control in the immunoblot experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. All uncropped immunoblotting images for this study are summarized in Figure S1.