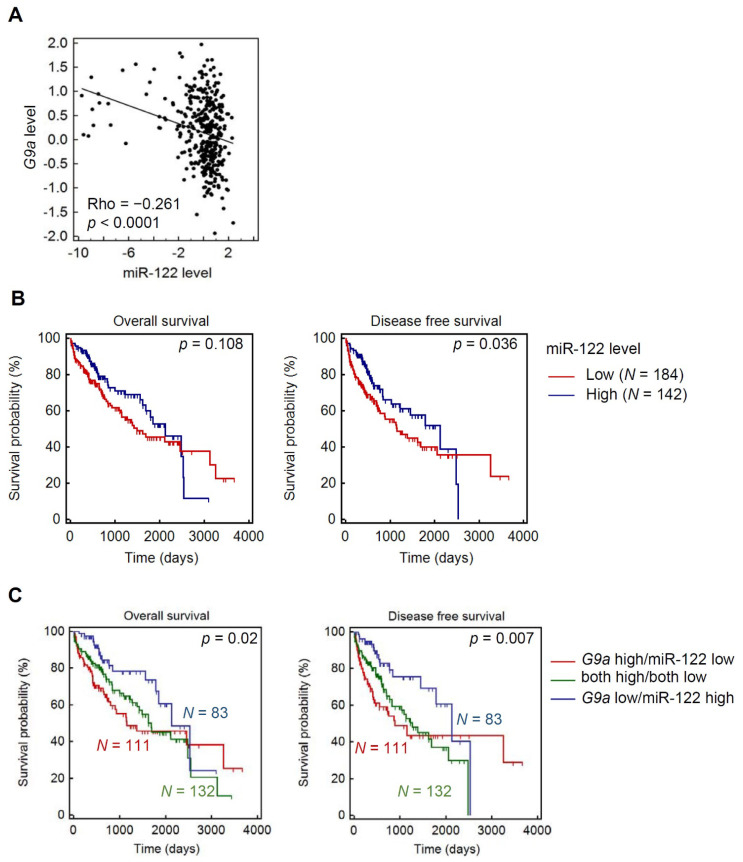
Figure 6.
Clinical significance of miR-122 and G9a in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) RNA expression scatter diagrams of G9a mRNA versus miR-122. Black dots represent expression levels of both genes from specimens in TCGA HCC dataset. Spearman’s non-parametric correlation test showing a negative correlation between G9a and miR-122 in HCC (Rho = −0.261, p < 0.0001). (B) Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) of patients with HCC, as categorized according to high or low expression levels of miR-122. The p-value indicates a comparison between patients with miR-122high and miR-122low. (C) All HCC patients were separated into a negative correlation of G9a and miR-122 expression, low miR-122 and high G9a, and high miR-122 and low G9a, and others (both high/both low). Data showed that patients in the G9ahigh/miR-122low group had the most favorable prognosis, including both OS and DFS.