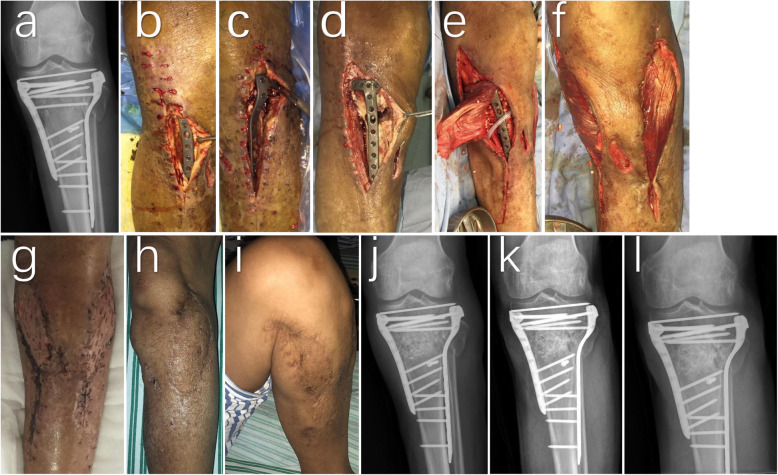
Fig. 1.
Typical case 1: Patient No. 14 presenting with plate exposure after tibial plateau fracture (Schatzker VI) surgery (b, c), The X-ray result shows the presence of local dead bone (a, red arrow). First, the necrotic tissue and inflammatory tissue (b, c) are completely removed. After removing the dead bone through the medial window, a 5 × 3 cm bone defect is found (d). The internal and external head muscle flaps of the gastrocnemius muscle are being designed and separated. The autologous iliac bone and the vancomycin/gentamicin-calcium sulfate-loaded artificial bone are being implanted into the bone defect (e). After covering the wound surface (f) of the leg with the internal and external cephalic muscle flaps from the gastrocnemius muscle, free skin grafting is performed on the surface of the muscle flap. Two weeks after operation, the skin graft survived and the incision healed well without swelling and exudation (g); The X-ray result shows that the bone graft was sufficient for the bone defect. The dead bone is also being removed (j). One year after operation, the patients recovered well (k). Two years after operation, the wound healed well and the knee joint flexion and extension function is good (h, i); The X-ray result shows that the fracture healed well (l)