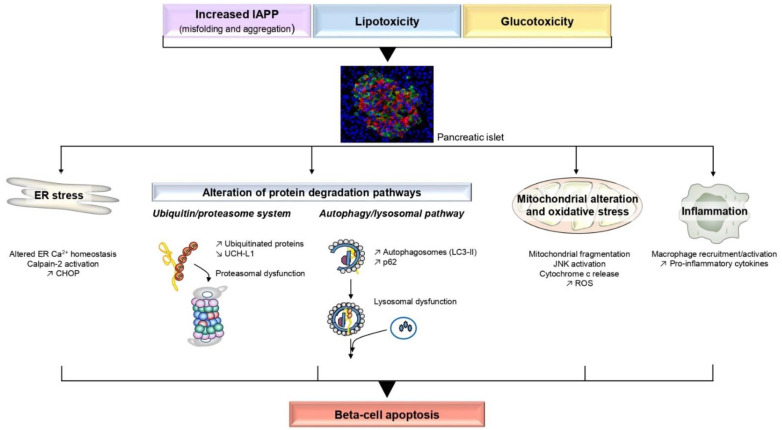
Figure 1.
Main mechanisms involved in pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis under T2D-prone situations. Increased islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) levels with misfolding and aggregation, lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity are the most investigated causative factors of beta-cell demise. These situations individually elicit stress pathways such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, mitochondrial/oxidative stress, inflammation, and disrupt the main pathways of protein clearance (ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy/lysosomal pathway). The synergistic deleterious effects of these situations as well as the crosstalk between the stress pathways ultimately contribute to beta-cell apoptosis. The immunofluorescence image is a human islet showing beta-cells in red and alpha-cells in green.