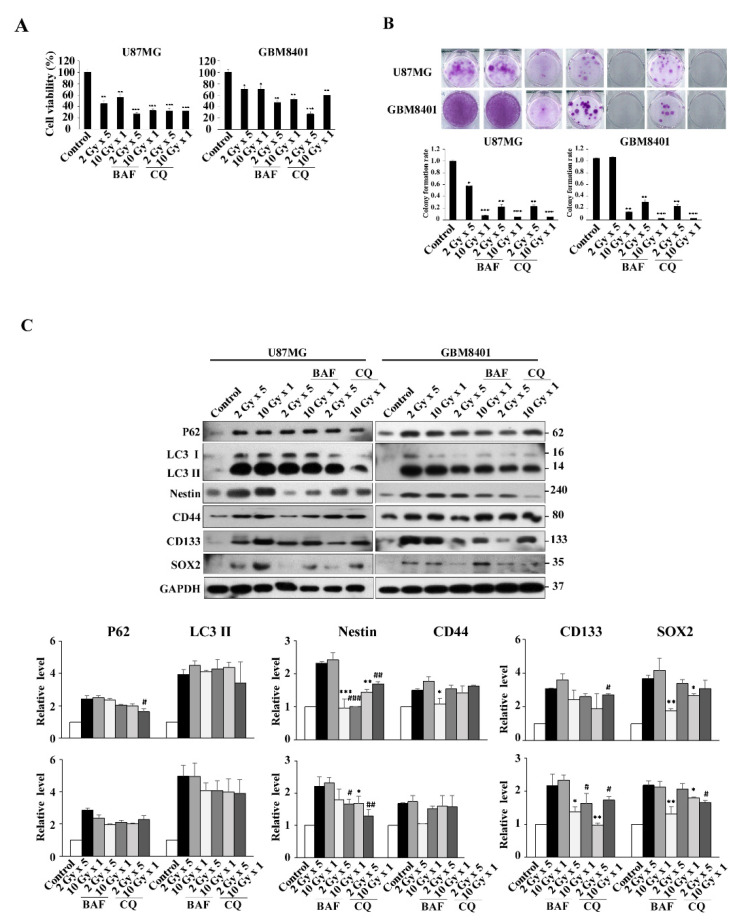
Figure 5.
Autophagy inhibition promotes radiation-induced cell death, and reduced radiation induced stemness in U87MG and GBM8401 cells. (A) Combination of radiation and autophagy inhibition with BAF (0.1 μM) or CQ (100 μM) decreased the U87MG and GBM8401 cell viability comparing with radiation only. (B) Clonogenic assays were performed to assess the effect of irradiation on colony formation in U87MG and GBM8401 cells with or without BAF (0.1 μM) or CQ (100 μM) treatment. The image shows colonies produced by the U87MG and GBM8401 cells following plating of 500 cells and 21 days incubation. Cells were quantified and error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. The level of significance was determined using Student’s t-Test with ns representing p > 0.05, *** p < 0.005, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05 compared with non-irradiated cells without BAF or CQ treatment. (C) Transcript levels of autophagic and CSCs-related genes were detected by Western blotting. Cells were irradiated, with or without BAF (0.1 μM) and CQ (100 μM) treatment for 72 h, followed by Western blot analysis of the autophagic and CSCs-related genes. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Bar graph represents mean of triplicates ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 compared with the 2 Gy × 5 times (10 Gy-fraction) group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 compared with the single dose 10 Gy (10 Gy-only) group.