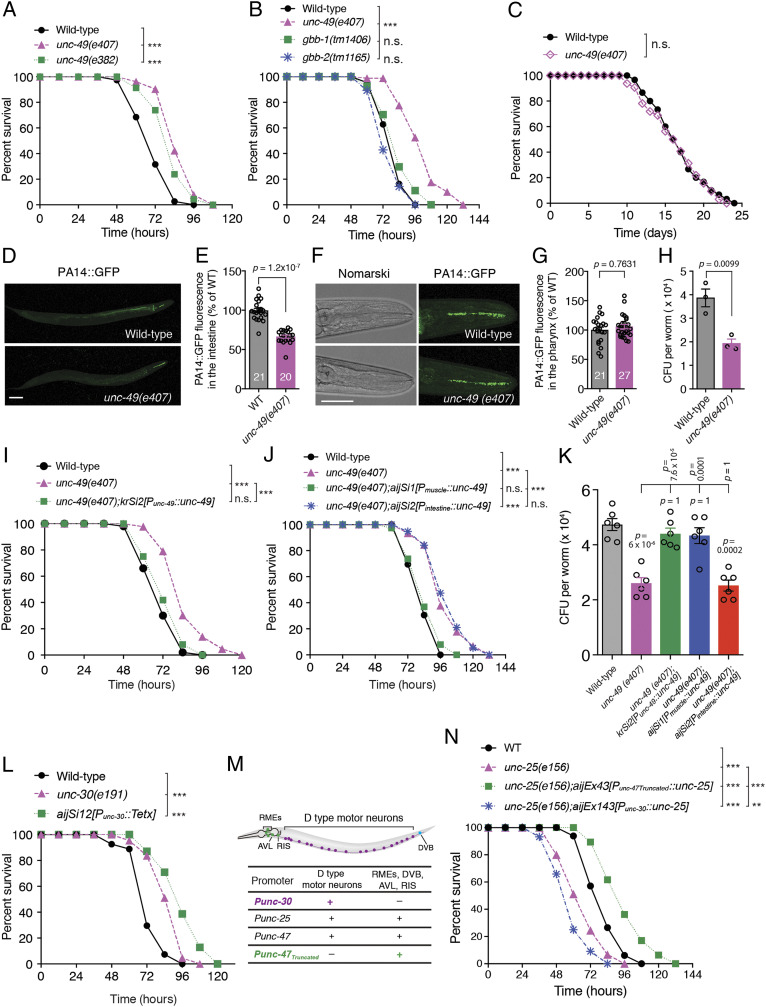
Fig. 1.
Deficiency in GABAergic NMJs extends survival of C. elegans upon P. aeruginosa PA14 exposure. (A–C) Survival of wild-type, unc-49(e407), and unc-49(e382) mutants (A) or of wild-type, unc-49(e407), gbb-1(tm1406), and gbb-2(tm1165) mutants (B) exposed to PA14 or of wild-type and unc-49(e407) mutants fed on heat-killed PA14 (C). The exact P values of statistics for all survival assays are listed in SI Appendix, Table S1. (D–G) Representative images (D and F) and fluorescence intensity (E and G) of wild-type and unc-49(e407) worms exposed to PA14-expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) for 24 h in the intestine (D and E) and pharynx (F and G) of animals. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The number of animals analyzed is indicated in E and G. (H) Quantitative analyses of the colony-forming units (CFU) of wild-type and unc-49(e407) worms exposed to PA14 for 24 h. (I–K) Survival (I and J) and CFU quantification (K) of wild-type, unc-49(e407), or indicated transgenic alleles for endogenous or tissue-specific rescue of unc-49(e407) worms exposed to PA14. (L) Survival of wild-type controls, unc-30(e191), and transgenic worms expressing the light chain of tetanus toxin (TeTx) under the control of the GABAergic D-type motor neuron-specific unc-30 promoter exposed to PA14. (M) Chart of GABAergic neuron expression patterns controlled by the corresponding specific promoters. (N) Survival of wild-type, unc-25(e156), and unc-25(e156) worms expressing UNC-25 in GABAergic non–D-type motor neurons under the control of an unc-47 truncated promoter (29) and in D-type motor neurons under unc-30 promoter, respectively, exposed to PA14. Statistical significance was determined by log-rank test for survival assays or nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test (E and G) or unpaired Student’s t test (H) or one-way ANOVA tests followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests (K). ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant. (Scale bar, 100 μm in D and 50 μm in F.)