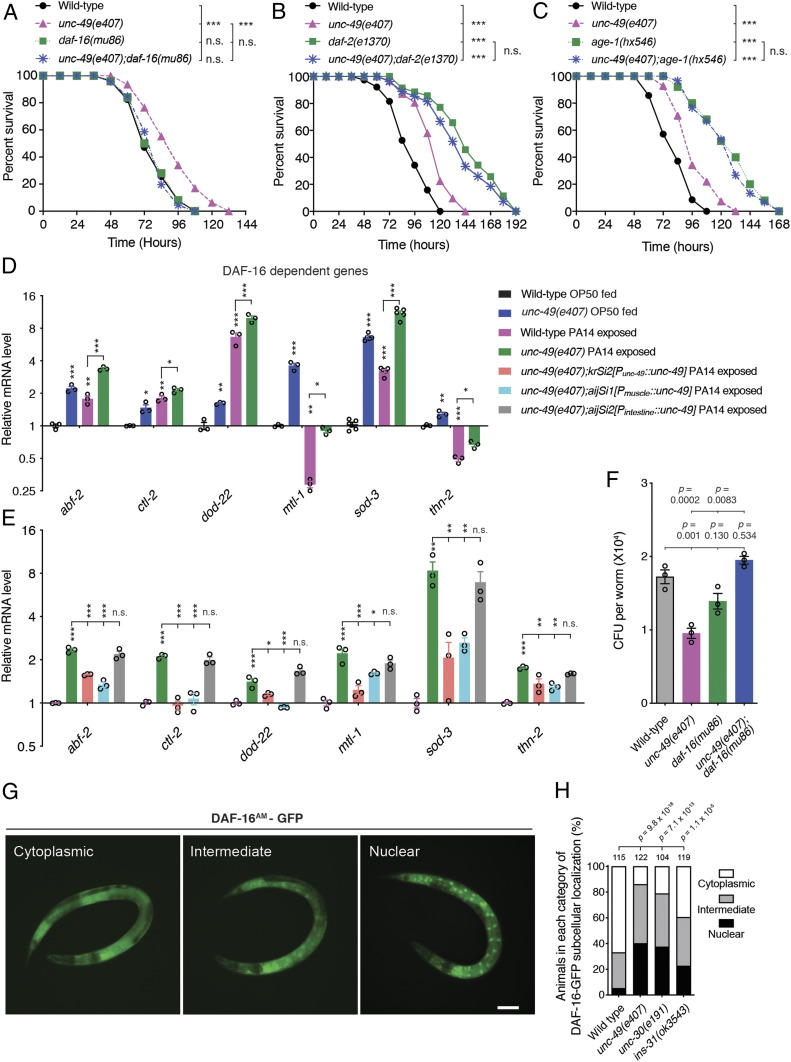
Fig. 3.
GABAergic synapse-mediated innate immunity is dependent on DAF-2/DAF-16 signaling. (A–C) Survival of wild-type, unc-49(e407), daf-16(mu86), and unc-49(e407);daf-16(mu86) (A) or wild-type, unc-49(e407), daf-2(e1370), and unc-49(e407);daf-2(e1370) (B) or wild-type, unc-49(e407), age-1(hx546), and unc-49(e407);age-1(hx546) (C) worms exposed to PA14. The exact P values of statistics for all survival assays are listed in SI Appendix, Table S1. (D and E) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of the expression levels of six DAF-16–dependent genes in wild-type and unc-49(e407) worms fed on OP50 or exposed to PA14 (D) or in wild-type, unc-49(e407), and unc-49(e407) mutant animals with GABAAR/UNC-49 expressed under the control of endogenous (krSi2[Punc-49::unc-49]), muscle (aijSi1[Pmyo-3::unc-49])-, or intestine (aijSi2[Pges-1::unc-49])-specific promoters exposed to PA14 (E). The exact P values of statistics for comparison of qRT-PCR between groups are listed in SI Appendix, Table S2. (F) CFU quantification of wild-type, unc-49(e407), daf-16(mu86), and unc-49(e407);daf-16(mu86) animals. Data are presented as means ± SEM. (G and H) The representative images of three categories (G) and quantification analysis (H) of nuclear accumulation of DAF-16aAM−GFP in wild-type, unc-49(e407), unc-30(e191), and ins-31(ok3543) mutant animals, respectively. Statistical significance was determined by log-rank test for survival assays or one-way ANOVA tests followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests (D, E, and F) or χ2 test (H). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant. (Scale bar, 100 μm in G.) The number of animals analyzed is indicated in H.