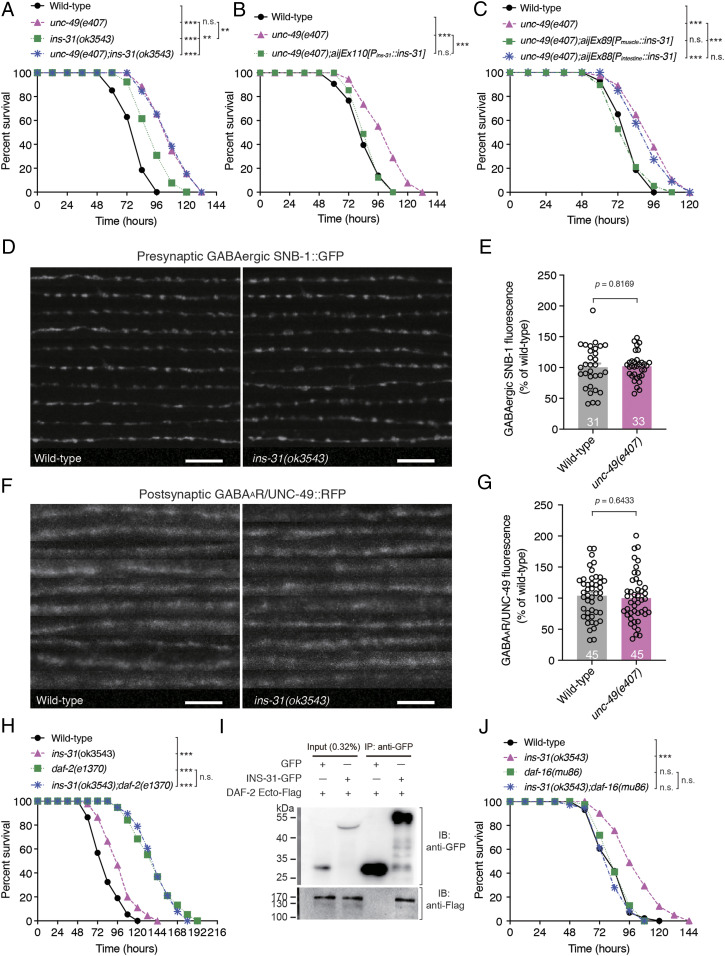
Fig. 6.
INS-31 acts downstream of GABAergic transmission and upstream of DAF-2 in intestinal innate immunity. (A) Survival of wild-type, unc-49(e407), ins-31(ok3543), and unc-49(e407);ins-31(ok3543) animals exposed to PA14. (B and C) Survival of wild-type, unc-49(e407), and transgene-expressing INS-31 under the control of endogenous (B), muscle (Pmyo-3)-, or intestine (Pges-1)-specific promoters (C), respectively, in ins-31(3543) animals exposed to PA14. (D–G) Ten representative images (D and F) and fluorescence intensity (E and G) of presynaptic GABAergic SNB-1::GFP (D and E) and postsynaptic GABAAR/UNC-49::red fluorescent protein (RFP) (F and G) in wild-type and ins-31(ok3543) animals, respectively. (H) Survival of wild-type, ins-31(ok3543), daf-2(e1370), and ins-31(ok3543);daf-2(e1370) animals exposed to PA14. (I) Immunoprecipitation of INS-31−GFP with anti-GFP antibodies followed by Western blot analysis with anti-Flag antibodies to detect the Flag-tagged extracellular domain of DAF-2 (DAF-2Ecto−Flag) from culture supernatant of human embryonic kidney 293 cells cotransfected with the plasmids encoding INS-31–GFP and DAF-2Ecto–Flag, respectively. (J) Survival of wild-type, ins-31(ok3543), daf-16(mu86), and ins-31(ok3543);daf-16(mu86) animals exposed to PA14. Statistical significance was determined by log-rank test for survival assays or unpaired Student’s t test (E and G). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant. The number of animals analyzed is indicated. (Scale bar, 10 μm.)