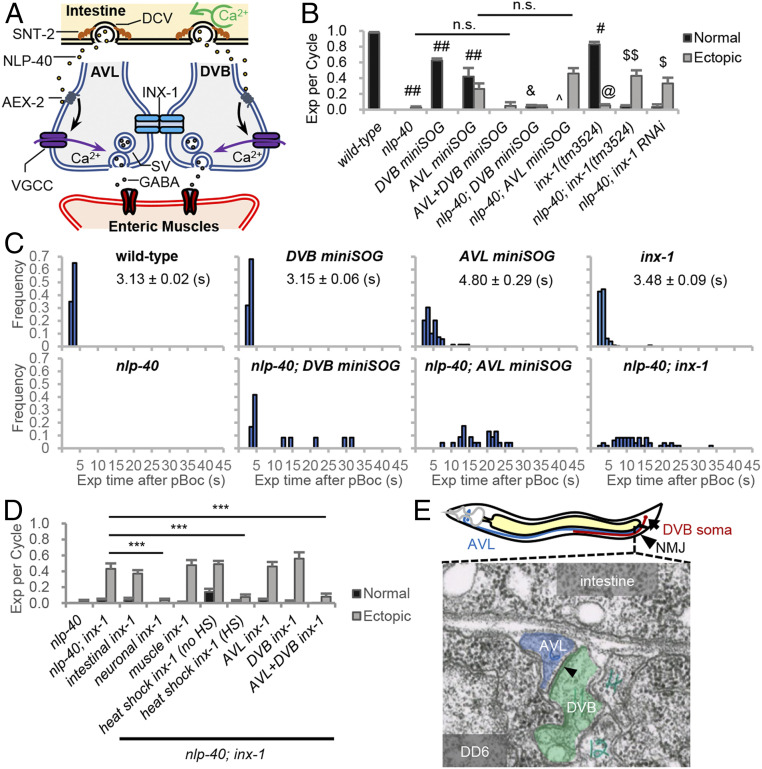
Fig. 1.
inx-1 functions in AVL and DVB motor neurons to regulate the frequency and timing of expulsion during the DMP. (A) Model for the circuit regulating expulsion (Exp). Calcium oscillations in the intestine (pacemaker) every 50 s lead to SNT-2/synaptotagmin-dependent secretion of NLP-40 from dense core vesicles (DCVs). NLP-40 activates the GPCR, AEX-2, in AVL and DVB, leading to calcium spike generation through VGCCs and GABA release from NMJs, which leads to the enteric muscle contraction. AVL and DVB NMJs are functionally coupled by INX-1/innexin, which coordinates AVL/DVB activities by suppressing ectopic calcium influx and promoting NLP-40-dependent AVL/DVB activation. (B) Quantification of the number of Exp per DMP cycle in adult worms with the indicated genotypes. “Exp per cycle” denotes the ratio of Exp per pBoc, which defines the start of the DMP. “Normal” denotes Exp occurring less than 5 s after pBoc, and “Ectopic” denotes Exp occurring more than 5 s after pBoc. DVB miniSOG and AVL miniSOG denote transgenes expressing miniSOG under control of a flp-10 and flp-22 promoter fragment, respectively. (C) Histograms showing the time when each Exp occurred after pBoc in the indicated strains. The average Exp time after pBoc with SEs is shown for wild-type, DVB miniSOG, AVL miniSOG, and inx-1 mutants. (D) Quantification of the number of Exp per DMP cycle in adult nlp-40 mutants, nlp-40; inx-1 mutants or nlp-40; inx-1 mutants expressing the indicated transgenes. “intestinal inx-1” denotes full length inx-1a cDNA expressed under the intestine-specific nlp-40 promoter. “neuronal inx-1” denotes inx-1a cDNA expressed in GABAergic neurons using the unc-47 promoter. “muscle inx-1” denotes inx-1a cDNA expressed in body wall muscles using the myo-3 promoter. “heat shock inx-1” denotes inx-1a cDNA expressed using the heat shock promoter (Phsp-16.2) either without or with heat shock for 1 h at 34 °C. DVB inx-1 and AVL inx-1 denote transgenes expressing inx-1a cDNA under control of the flp-10 and flp-22 promoter, respectively. (E) (Above) Diagram showing the cell bodies and axons of AVL/DVB and the NMJ region of AVL/DVB in the preanal ganglia. (Below) Transmission electron micrograph image of AVL and DVB axons in cross section in the preanal ganglion region (image JSE_207, also known as JSE_122116), showing a large gap junction (arrowhead) between AVL and DVB axons. The gap junction appears as electron dense areas within the plasma membranes of AVL and DVB where they contact each other. DD6 refers to the soma of the DD6 motor neuron. The electron dense regions of AVL and DVB plasma membranes are present in eight serial sections (JSE_205 to JSE_213). Adapted with permission from David Hall, Albert Einstein College of Medicine. Means and SEs are shown. Student’s t test: ***P < 0.001; ##P < 0.001 compared to wild type; #P < 0.01 compared to wild type; &P < 0.001 compared to DVB miniSOG; ^P < 0.01 compared to AVL miniSOG; $$P < 0.001 compared to nlp-40; $P < 0.01 compared to nlp-40; @P < 0.001 compared to wild type; n.s., not significant.