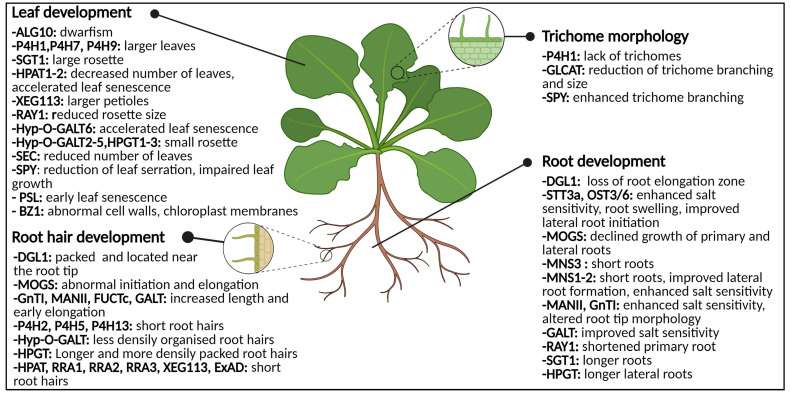
Figure 5.
Graphical representation of the glycosylation-related enzymes and their role in leaf development, trichome morphology and root (hair) development. Both abnormal N-glycosylation and O-glycosylation result in changes of phenotype and morphology. Abbreviations: ALG10 (α-1,2-glucosyltransferase 10), BZ1 (Brittle stem and Zebra Leaf 1), DGL1 (DEFECTIVE IN GLYCSOYLATION1), ExAD (extensin arabinose deficient transferase), FUCTc (α1,4-fucosyltransferase), GALT (β1,3-galactosyl-transferase), GLCAT (β-glucuronosyltransferases), GnT1 (N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I), HPAT1-2 (Hyp O-arabinosyltransferases 1 and 2), HPGT (Hydroxyproline O-galactosyltransferase), Hyp-O-GALT (hydroxyproline-O-β-galactosyltransferase), MANII (α-mannosidase II), MNS (α-mannosidase I), MOGS (mannosyloligosaccharide glucosidase), OST3/6 (oligosaccharyltransferase subunit 3/6), P4H (prolyl 4-hydroxylase), PSL (premature senescence leaf), RAY1 (REDUCED ARABINOSE YARIV1), RRA (REDUCED RESIDUAL ARABINOSE), SEC (SECRET AGENT), SGT (serine O-α-galactosyltransferase), SPY (SPINDLY), STT3a (STAUROSPORIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSITIVE3A), XEG113 (Xylo-endoglucanase113). This figure was created with BioRender.com.