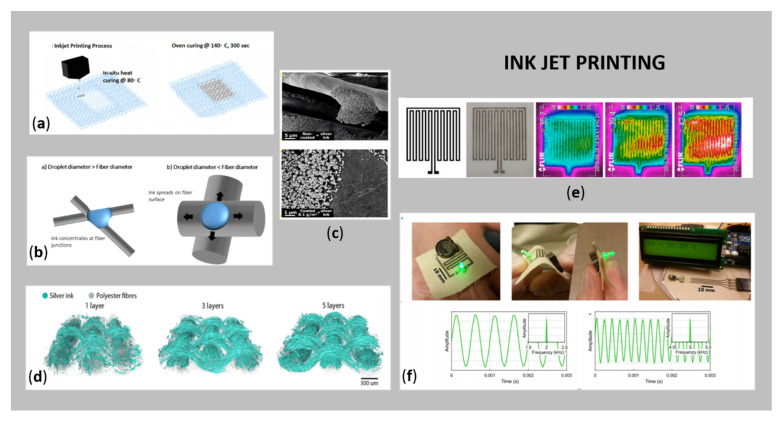
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic presentation of inkjet printing of conductive Ag ink on textiles (reprinted with permission from Ref. [37] Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society); (b) presentation of a drop of Ag ink distribution on fibers with different diameters (reprinted with permission from Ref. [37] Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society); (c) SEM images of Ag inkjet printing, together with a combination of cellulose nanofibrils/glycerol on woven cotton fabric (reprinted with permission from Ref. [50] Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society); (d) XCT 3D reconstruction images of Ag (blue-green) deposited on polyester fabric (grey) with an increasing number of layers (reprinted with permission from Ref. [51] Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society); (e) textile heating actuators—computer designed patterns and thermal images of Ag inkjet printing PP spun non-woven textile (reprinted with permission from Ref. [52] Copyright 2021, Elsevier); and (f) digital moisture sensor signals recorded from the inkjet printing part on the fabric (reprinted with permission from Ref. [50] Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society).