Figure 1.
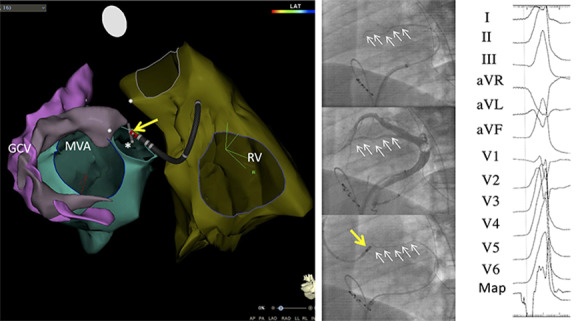
Intramural premature ventricular complex where the ablation catheter failed to reach the site of origin (SOO) and radiofrequency catheter ablation was carried out at a site located close to the SOO in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT). (A) 3-dimensional reconstruction of echocardiographic contours obtained by intracardiac echocardiography with posterior views of the right ventricle (RV), the left ventricle with the mitral valve annulus (MVA), and the great cardiac vein (GCV). The GCV and its continuation into the anterior interventricular veins (AIVs) is pink while the perforator vein is lavender. The ablation catheter is located in the LVOT (yellow arrow). A mapping wire (grey icon) is located in the distal perforator vein (asterisk). (B, top) Left anterior oblique (LAO) view showing selective cannulation of a perforator vein with a unipolar mapping wire (series of white arrows). (B, center) LAO view of an occlusive venogram showing the GCV, the AIV, and a perforator vein (series of white arrows). (B, bottom) LAO view with the mapping wire located in the proximal perforator vein (series of white arrows). The ablation catheter (yellow arrow) is placed in the LVOT in close proximity to the tip of the mapping wire that is indicating the location of the SOO. (C) A recording from the mapping wire that precedes the onset of the PVC-QRS complex by 40 msec. Radiofrequency ablation was successfully performed from the ablation catheter located in the LVOT (yellow arrow). Reprinted with permission from Ghannam et al.25
