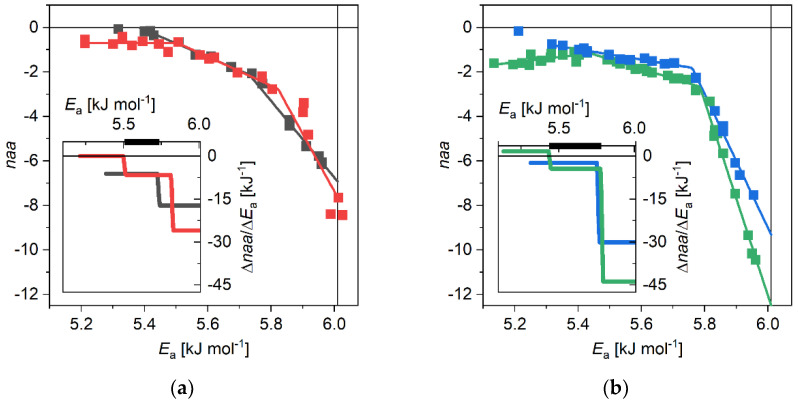
Figure 2.
(a) Oligomer-monomer melting diagrams for wild type (grey) and A53T (red) α-synuclein; (b) Amyloid-monomer melting diagrams for wild type (blue) and A53T (green) α-synuclein. Mol H2O per mol amino acid residue (naa) vs. potential barrier. Lines are guides to the eye. The insets are the derivative forms of the difference melting diagrams. The thick black lines denote the common sections on the derivative melting diagrams.