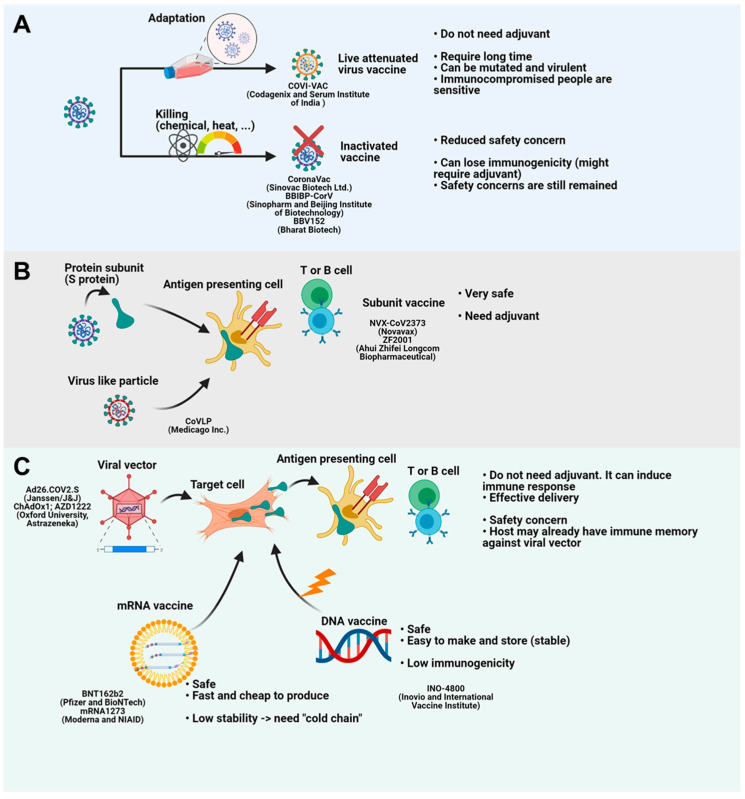
Figure 2.
Vaccine platforms for COVID-19. (A) Live attenuated vaccines are developed through repeated attenuation. Inactivated vaccines are generated by chemical or heat stress. Live attenuated vaccines do not require adjuvant. However, this technology takes a long time and has safety concerns. Inactivated vaccines have reduced danger compared to attenuated vaccines. However, they need adjuvant because they lose their immunogenicity. (B) Protein subunit vaccine or subunit-containing virus like particle (VLP) provides antigen to antigen presenting cells (APCs). APCs present antigen to immune cells and generate immune memory. Although these platforms are safe, they need adjuvant. (C) Viral vector vaccines deliver antigen-coding genes to target cells. Infected cells make and give antigen to APCs. Viral vectors do not need adjuvant because the vector itself is danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP). Delivery is also easy. However, they have safety concerns and vectors can be eradicated by host immune memory if the host has experience of the viral vector. mRNA vaccine and DNA vaccine deliver mRNA and DNA to the target cells. mRNA and DNA generate antigens. While mRNA vaccines are safe, fast and cheap, they need “cold chain” because RNA is unstable. DNA vaccines are stable and safe. However, they are weak to induce proper immunity. Figure was created by biorender.com (BioRender, Toronto, ON, Canada).