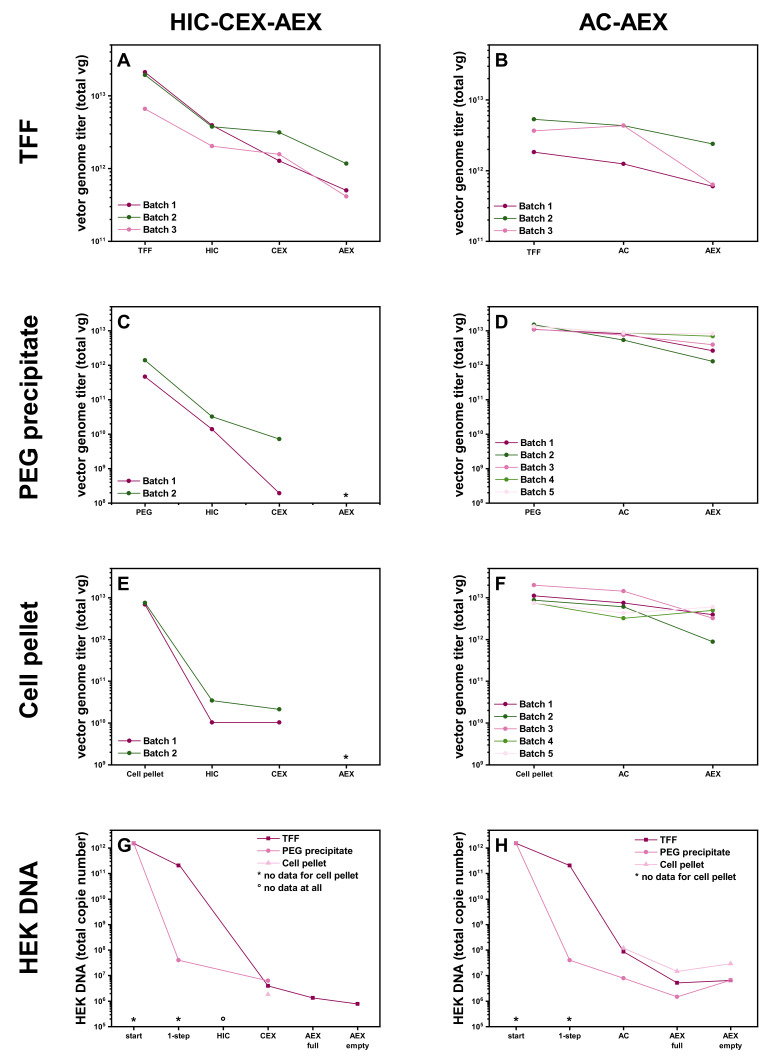
Figure 3.
Effect of different harvesting methods on the rAAV2/8 vector production yield and pureness of the human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cell DNA. (A–F) Graphs showing the yield (total vector genomes, vg) for the rAAV2/8 vectors obtained with the two strategies, with materials harvested from (A,B) the cell culture supernatant and cell pellet lysate filtered, concentrated, and buffer-exchanged by tangential flow filtration (TFF) (n = 3). (C,D) Culture supernatant by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation (C), followed by HIC-CEX (n = 2) and (D) followed by AC-AEX (n = 5) or (E,F) cell pellet lysate (E) followed by HIC-CEX (n = 2) and (F) followed by AC-AEX (n = 5). (G,H) Graphs showing the removal efficiency of the strategies for HEK cell DNA at all the purification steps. AC, affinity chromatography; AEX, anion exchange chromatography; CEX, cation exchange chromatography; HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography; PEG, polyethylene glycol; rAAV, recombinant adeno-associated virus.