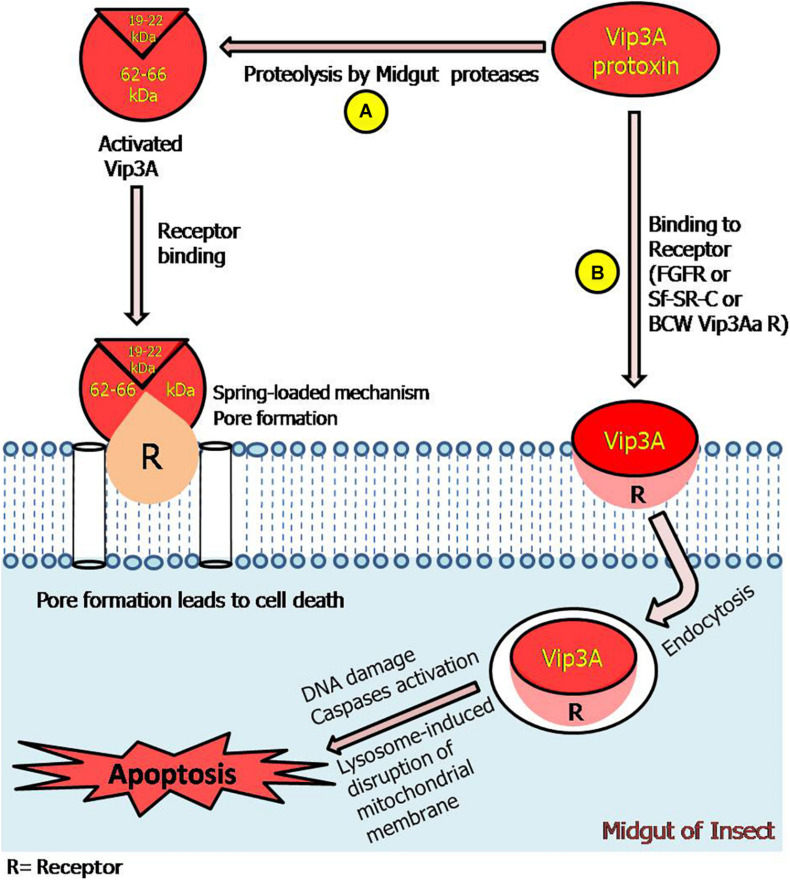
FIGURE 5.
Model representing Vip3A proteins-insecticidal mechanism through pore formation and apoptosis. (A) The ∼62–66 kDa fragments along with ∼19–22 kDa fragment can bind with receptors leading to pore formation and cell death. (B) This represents that Vip3A-protoxin can bind to all three specific receptors in the target insect. Thereafter, enter the cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis and induced activation of caspases, DNA damage, and lysosome-induced disruption of the mitochondrial membrane which leads to apoptosis process in Sf9 cells and ultimately insect mortality. However, the responsible signaling pathway is still undefined.