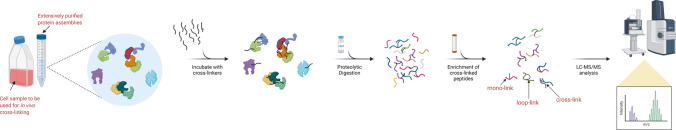
Fig. 3.
The XL-MS workflow. Chemical crosslinking can be performed in vitro using extensively purified protein assemblies or in vivo using intact cells. The first step of chemical crosslinking involves adding a selected crosslinker to the protein mixture or cells. After chemical crosslinking, crosslinked proteins are digested to yield peptides. Typically, three types of cross-linked peptides are produced, i.e., the mono-linked peptides, the loop-linked peptides and the cross-linked peptides, among the many unlabelled peptides and unreacted crosslinkers. Due to the heterogeneity, the total pool of proteolyzed peptides is subjected to fractionation to enrich cross-linked peptides, subsequently mass-analysed by LC–MS/MS