Fig. 1 a.
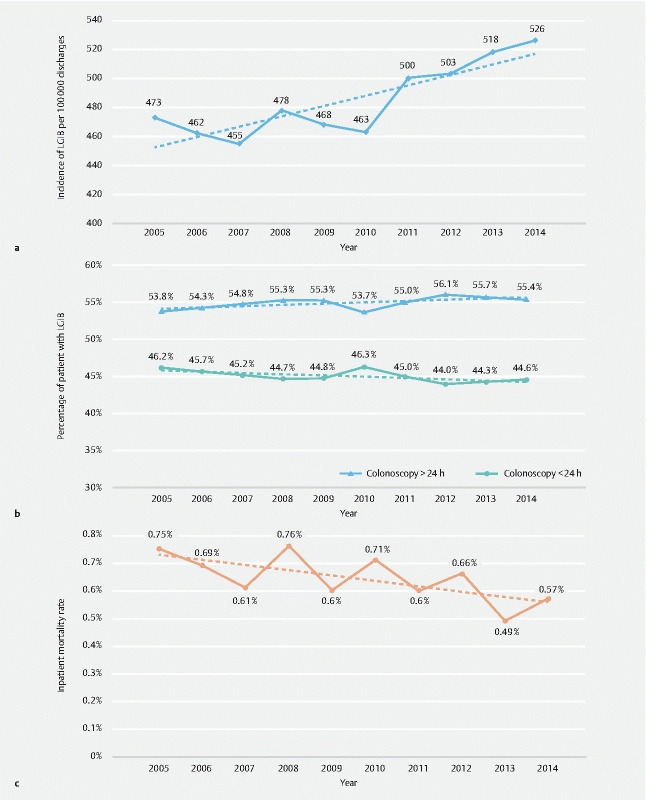
Trends for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB). The figure depicts the number of patients with LGIB admitted per 100,000 hospital discharges over the study period from 2005 to 2014 and shows rising incidence of LGIB admissions ( P trend < 0.001). b Trends for colonoscopy timing among patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB). The proportion of patients having early or late colonoscopy over the study period are shown. Both trends of timing are statistically non-significant (early colonoscopy P trend = 0.07, late colonoscopy P trend = 0.06). c Trends for inpatient mortality in LGIB over the study period. The rates of inpatient mortality from 2005 to 2014 in the study cohort are shown ( P trend < 0.001).
