Figure 3. Chemically resistant aquaplastic and their templated surface structure properties.
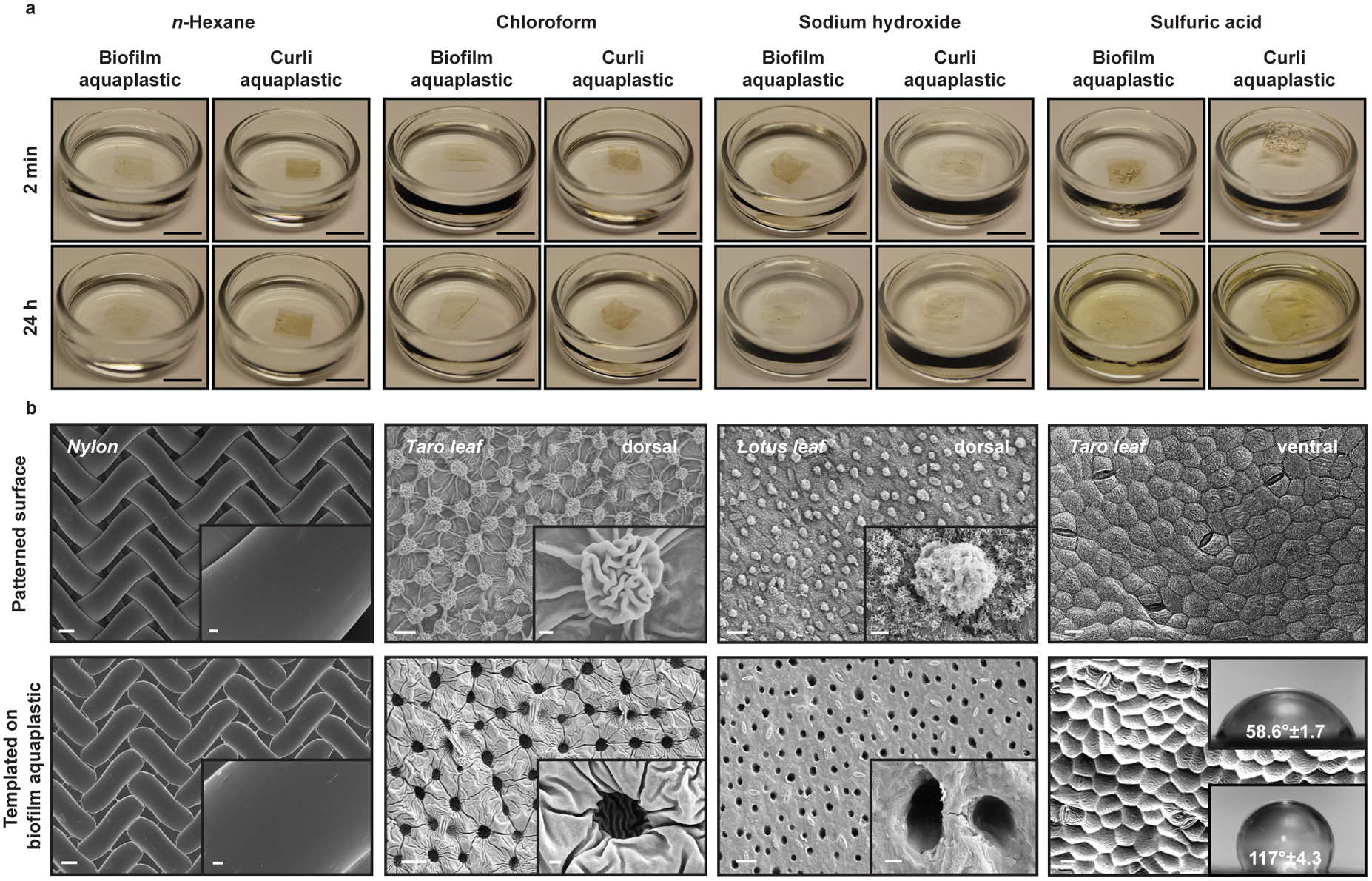
a. Images showing the stability of a 1 cm2 sample of aquaplastic in organic solvents (n-hexane, chloroform), strong acid (98% sulfuric acid) and strong base (18M sodium hydroxide) after 2 minutes or 24 hours of exposure. Scale bar, 1 cm. b. FESEM images show the patterns transferred (bottom row) on biofilm aquaplastic by templating biofilm aquagel on various surfaces (top row) by ambient drying. Scale bar, 20 μm. Insets in the first three columns show higher magnification of surface features. Scale bar, 2 μm. Insets in the last column are water contact angles for non-templated (top) and templated aquaplastic surfaces (bottom), showing increased hydrophobicity.
