Figure 5. Reduced cholesterol efflux capacity in ADAM17-deficient macrophages reflects inhibition of TNFα-induced ABCA1 expression.
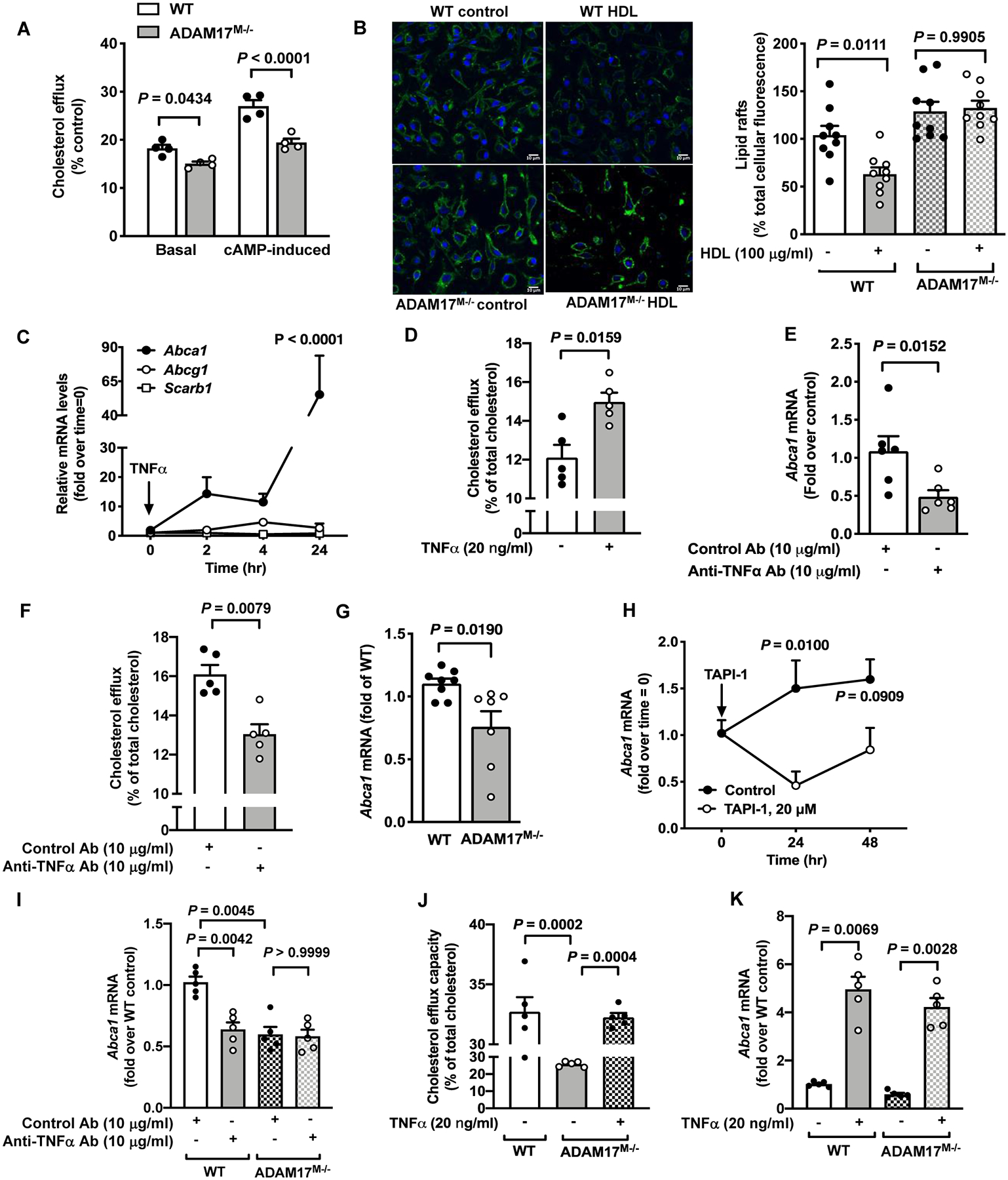
A. BMDMs from male C57BL/6J WT and ADAM17-deficient mice were loaded with radiolabeled [3H]-cholesterol and then treated with HDL (100 μg/ml) for 4 hr. Cholesterol efflux capacity was determined in cAMP-stimulated or unstimulated cells treated with an acyl–coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor (n=4). B. BMDMs from male WT and ADAM17-deficient mice treated with HDL (100 μg/ml) for 18 hr. At the end of the treatment, the cells were fixed and stained for lipid rafts with cholera toxin B. Representative pictures and quantification of lipid raft staining are shown (n=9). C. BMDMs from female C57BL/6J mice were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for indicated periods of time. RNA extracts were prepared, and mRNA levels of Abca1, Abcg1 and Scrab1 were analyzed by real-time PCR (n=4; experiment performed twice with similar results). P-value represents changes compared to time point 0. D. BMDMs from male C57BL/6J mice were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) and cholesterol efflux was determined as in A (n=5). E. A neutralizing anti-TNFα antibody or a control antibody were used to treat BMDMs from male C57BL/6J mice for 4 hr. RNA extracts were used to measure Abca1 gene expression (n=6). F. Cholesterol efflux was measured in cells from male C57BL/6J mice treated with a neutralizing anti-TNFα antibody or a control antibody (n=5). G. BMDMs from male WT and ADAM17M−/− mice were analyzed for Abca1 gene expression after 7 days of differentiation (n=7–8). H. BMDMs from female C57BL/6J mice were treated with TAPI-1 (20 μM) for 24 and 48 hr. At the end of stimulation, cells were analyzed for Abca1 gene expression (n=3–5; experiment performed twice with similar results). I. BMDMs from male WT and ADAM17M−/− mice were treated with a neutralizing anti-TNFα antibody or a control antibody, and Abca1 mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR (n=5). J. WT and ADAM17-deficient BMDMs from male mice were incubated with or without TNFα, and cholesterol efflux capacity was then measured as in A (n=5). K. BMDMs from WT and ADAM17M−/− male mice were treated with and without TNFα (20 ng/ml) for analysis of Abca1 mRNA levels (n=5; experiment performed twice with similar results). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Tests for normality (Shapiro-Wilk) and equal variance (Brown-Forsythe) were performed for each of the data sets. P values were determined accordingly by two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison tests (A, H) or Tukey’s multiple comparison tests (C, J), unpaired two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (D, E, F, G) or by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests (B) or Brown-Forsythe ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests (I, K). Unless otherwise stated, data are representative of at least three independent experiments performed in replicates in BMDMs from male mice.
