Figure 1. Decreased expression of DLX3 correlates with skin cancer progression and poor survival in patients.
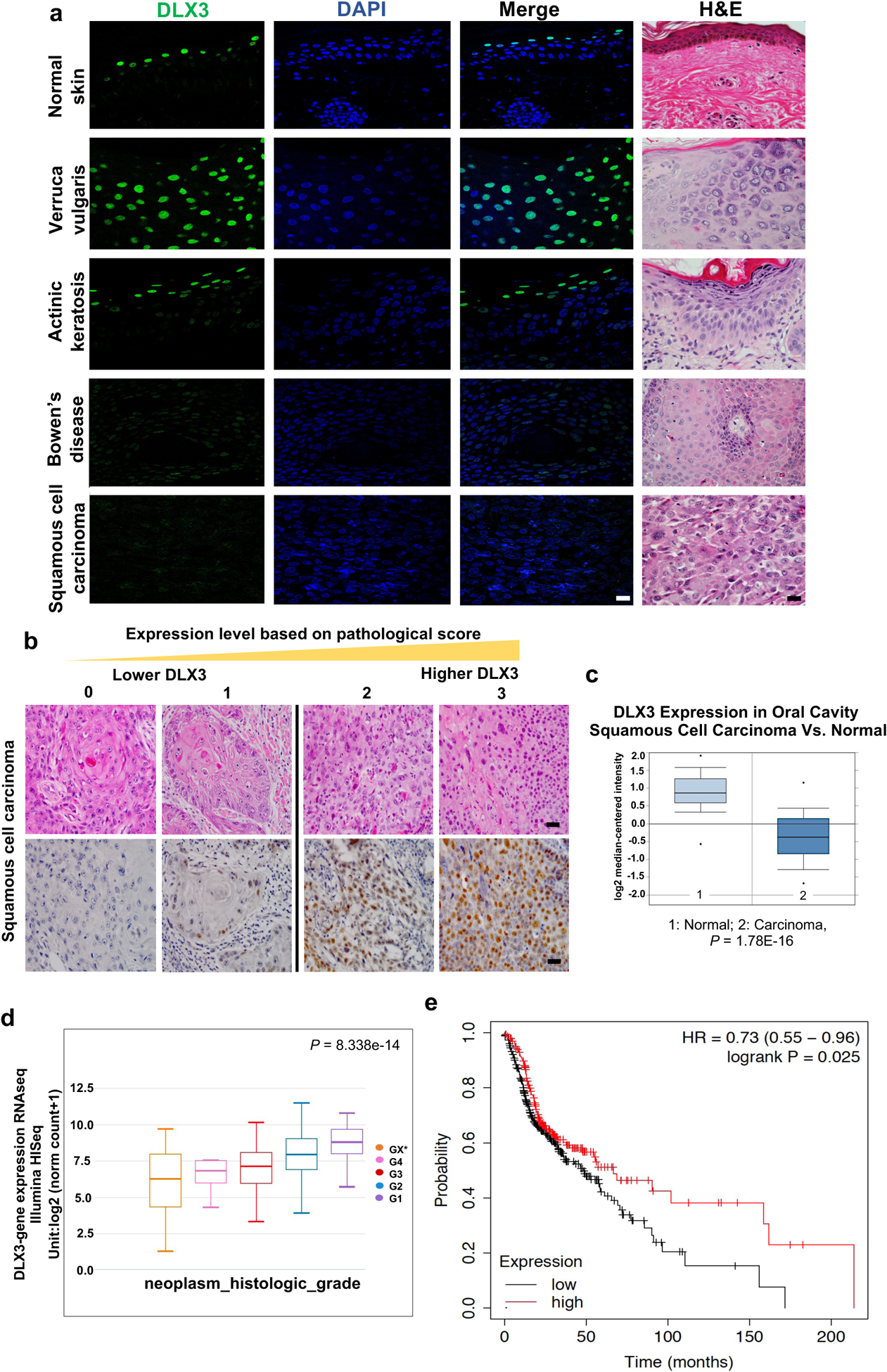
(a) Immunofluorescence and Hematoxylin/eosin (H&E) staining using antibodies specific for DLX3. (Scale bar: 25μm). A total of 121 SCC patient samples and six benign skin tumors were stained and analyzed. (b) Representative H&E and immunohistochemical staining of DLX3 in SCC with a reactivity score of 0 to 3. (Scale bar: 50μm). Pathological score was defined as: 0, ≤ 10% of tumor area stained; 1, 11–25% stained; 2, 26–50% stained; 3, ≥51 % stained. Tumors scoring 2 and 3 were defined as high-expression tumors. (c) Box-plots showing DLX3 expression level is significantly decreased in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma [1=Normal; 2=Squamous Cell Carcinoma] as determined by TCGA Database. (d) Box-plots showing Dlx3 expression in HNSCC samples determined by TCGA Database. G1 to G4 indicate increase in tumor stages. *Grading could not be defined. [P-value=8.338e–14]. (e) Survival of hnSCC patients according to the expression profile of Dlx3 mRNA in 500 patients with available clinical data (Source data: Kaplan-Meier Plotter, Pan-cancer RNA-seq, https://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=pancancer_rnaseq). The logrank P-value is indicated on the graph.
