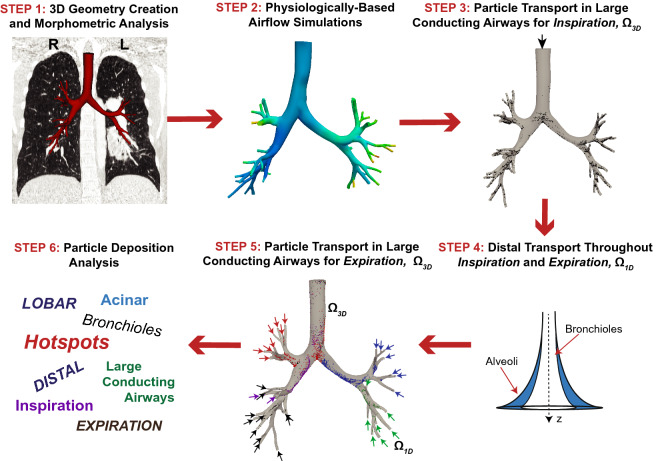
Figure 1.
Simulation pipeline for the multi-dimensional airflow and transport simulations. Airway geometries were previously created from CT images and airway morphometry was measured from the geometric models (Step 1)34. In Oakes et al.34 airflow was simulated throughout the respiration cycle by a pressure differential that overcame the respiratory resistance and compliance to drive air in and out of the lungs (Step 2). Particles are then tracked throughout the respiration cycle by first calculating their individual trajectories in the 3D models for inspiration (Step 3). Next, the aerosol bolus is convected through the distal regions of the lung by solving reduced-order models with a deposition loss term (Step 4). Finally, the particle trajectories are solved throughout expiration in the 3D airways (Step 5) and the regional deposition patterns are assessed (Step 6).