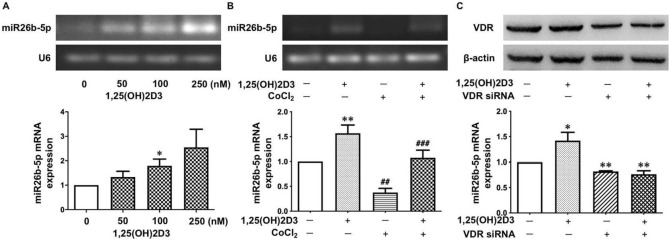
Figure 5.
Vitamin D promotes miR-26b-5p expression in placental trophoblasts. (A) 1,25(OH)2D3 stimulates miR-26b-5p expression in HTR-8/SVneo cells. The bar graphs show relative miR-26b-5p expression after normalization to U6 expression in each sample from seven independent experiments. *P < 0.05: 100 nM of 1,25(OH)2D3 treated vs control. (B) miR-26b-5p expression in HTR-8/SVneo cells treated with CoCl2 in the presence or absence of 1,25(OH)2D3, showing that 1,25(OH)2D3 could prevent the CoCl2-induced decrease in miR-26b-5p expression in placental trophoblasts. The bar graphs show relative miR-26b-5p expression after normalization to U6 expression in each sample from eleven independent experiments. **P < 0.01: 1,25(OH)2D3 treated vs control. ##P < 0.01: CoCl2 alone vs control. ###P < 0.001: 1,25(OH)2D3 + CoCl2 vs CoCl2 alone. (C) Inhibition of VDR expression prevents 1,25(OH)2D3-induced increase in miR-26b-5p expression in placental trophoblasts. VDR siRNA was transfected into HTR-8/SVneo cells. The bar graphs show relative miR-26b-5p expression after normalization to U6 in each sample from four independent experiments. *P < 0.05: 1,25(OH)2D3 treated vs control. **P < 0.01: VDR siRNA and 1,25(OH)2D3 + VDR siRNA vs 1,25(OH)2D3 treated alone, respectively.