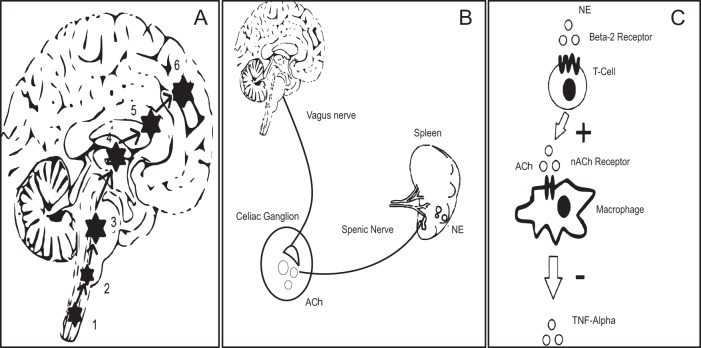
Fig. 5. Putative mechanism of nVNS action at circuit level and cellular level.
The pathway of direct stimulation of brain regions. 1&2, Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and nucleus tractus solitarius; 3, Locus coeruleus; 4&5, Basal ganglia and thalamus; 6, forebrain cholinergic nucleus (including nucleus basalis of Meynert). B inflammatory reflex through vagus nerve showing the efferent limb. Vagus nerve stimulation leads to secretion of ACh in the celiac ganglion. ACh in turn stimulates the splenic nerve, which provides direct adrenergic innervation to the spleen. [Ach = Acetyl Choline; NE = Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline]. C The cellular and molecular environment inside the spleen. NE secreted by splenic nerve stimulates T cells (cholinesterase positive to secrete Ach). The secreted neurotransmitter binds with the 7-α subunit of nicotinic ACh receptors on the surface of macrophages and inhibits secretion of TNF-α.