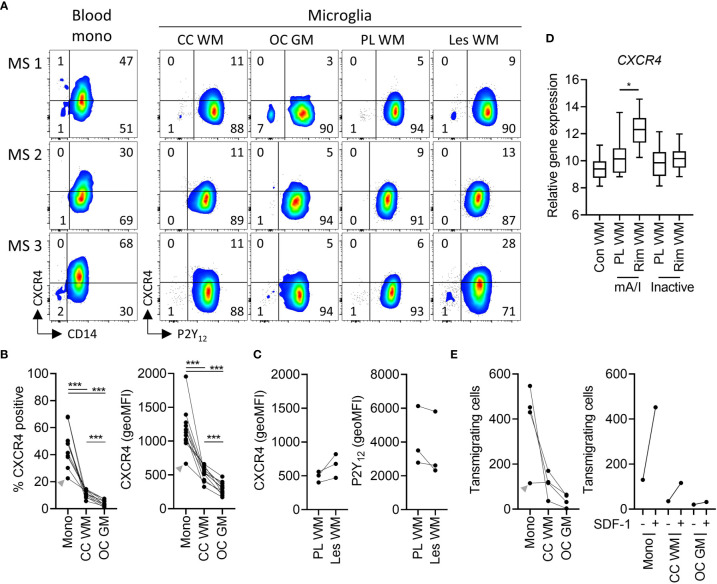
Figure 4.
Expression of functional CXCR4 in white and grey matter microglia in health and MS. (A) Representative dot plots of CXCR4 expression on paired peripheral CD14+ blood monocytes and P2Y12 + microglia from corpus callosum white matter and occipital cortex grey matter, as well as P2Y12 + microglia from peri-lesional and lesional subcortical WM of three MS brain donors measured by flow cytometry. (B) Quantification of CXCR4 expression (percentage of positive cells and geoMFI) on monocytes, WM microglia, and GM microglia of n=11 brain donors (3 MS, 8 non-MS; Wilcoxon-signed rank test; ***p < 0.0005). (C) Quantification of CXCR4 and P2Y12 expression on microglia from peri-lesional and lesional WM of three MS brain donors. (D) Quantification of tissue gene expression of CXCR4 in control as well as peri-lesional and lesional WM from mixed active/inactive and inactive MS lesions (18) (Wilcoxon-signed rank test; *p < 0.05). (E) Quantification of transwell migration of monocytes, white matter microglia, and grey matter microglia in response to the CXCR4 ligand SDF-1 of n=4 brain donors (left panel). Of note, SDF-1-stimulated transwell migration was higher as compared to spontaneous transwell migration in all three cell types (n=1 brain donor; right panel). A donor with a relatively low expression of CXCR4 on monocytes also showed low monocyte transmigration towards SDF-1 (grey arrowhead). mono, monocytes; CC, corpus callosum; WM, white matter; OC, occipital cortex; GM, grey matter; PL, peri-lesional; Les, lesional; mA/I, mixed active/inactive; geoMFI, geometric mean fluorescence intensity.