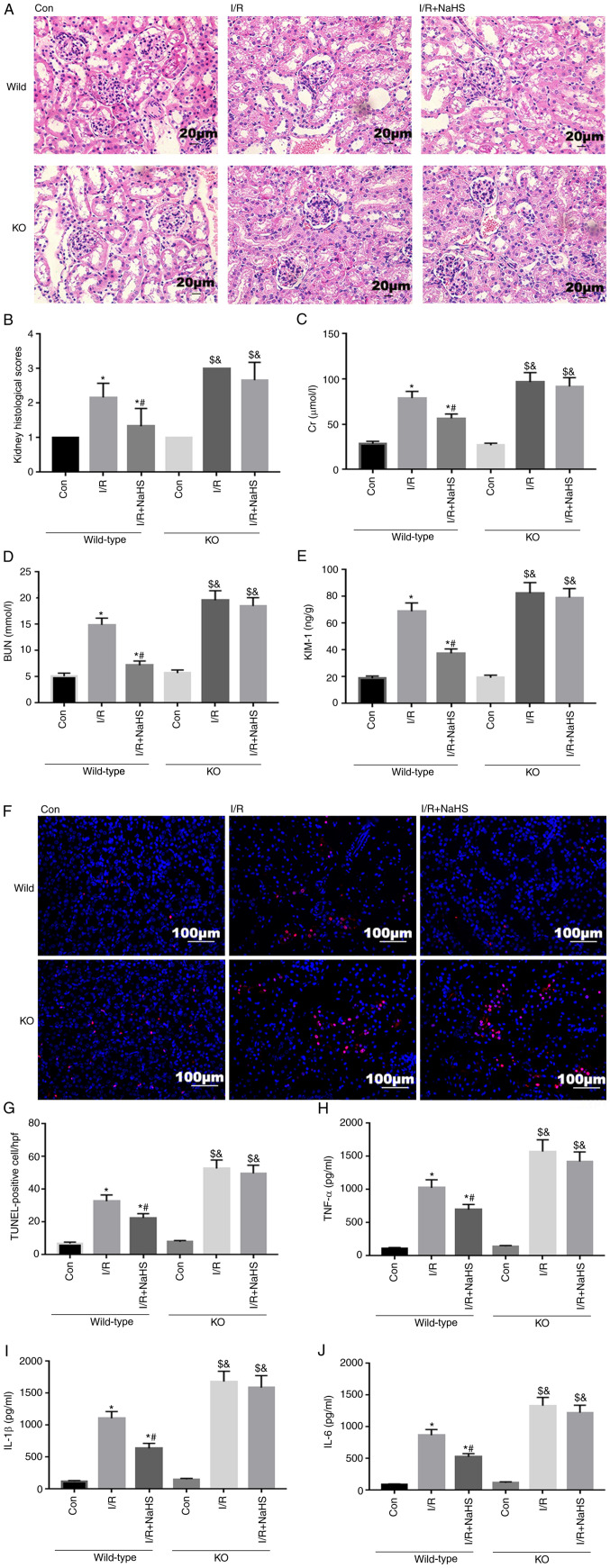
Figure 7.
NaHS alleviates renal dysfunction, excessive release of cytokines and cell apoptosis induced by renal I/R via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Wild-type and Nrf2-KO mice underwent surgery to induce renal I/R via clamping of the bilateral renal pedicles. Mice were treated with 50 µmol/kg intraperitoneal NaHS prior to renal ischemia. (A) At 24 h post-reperfusion, blood and renal tissue were collected to measure (B) histopathological changes and (C) Cr, (D) BUN and (E) KIM-1 levels. Scale bar, 20 µm. (F and G) Apoptosis and expression levels of (H) TNF-α, (I) IL-1β and (J) IL-6 were assessed. Scale bar, 100 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n=3). *P<0.05 vs. Con wild-type mice; #P<0.05 vs. I/R wild-type mice; &P<0.05 vs. I/R+NaHS wild-type mice; $P<0.05 vs. Con KO mice. NaHS, sodium hydrosulfide; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; KO, knockout; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule-1; Con, control; Cr, creatinine.