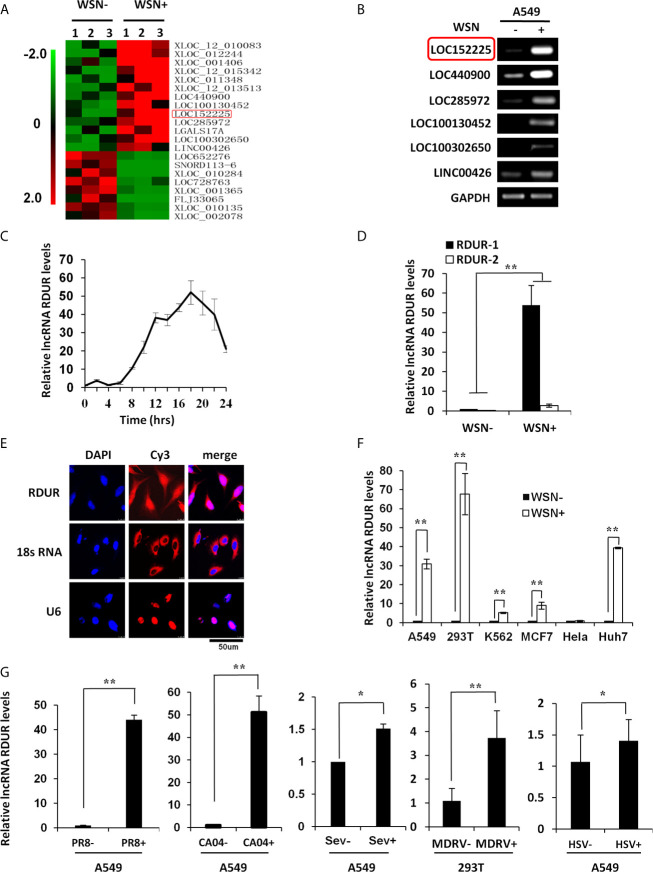
Figure 1.
Human RDUR is identified as a new lncRNA induced by influenza A virus and several other viruses. (A) The differentially expressed lncRNAs in A549 cells infected with or without A/WSN/33 influenza virus (WSN) were analyzed by a cDNA microarray (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/; GEO access number GSE58741). Shown are representative differentially expressed lncRNAs. (B) A549 cells infected with WSN were collected at 16 h post-infection (hpi). The differential expressions of 6 selected lncRNAs were confirmed by RT-PCR. RDUR (LOC152225) is indicated by red rectangle. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to examine the kinetics of RDUR expression in WSN infected A549 cells (n = 3; means ± SD). (D) Shown is the abundance of two isoforms of RDUR examined by qRT-PCR. The error bars represent the SD. Shown are representative results from three independent experiments. (E) RNA-FISH was performed to determine the localization of RDUR in WSN infected A549 cells. Shown were representative images from at least three independent experiments with similar results. (F) RDUR expression was examined by RT-PCR in indicated human cell lines infected with WSN (moi=1) for 16 h. Plotted are the average results from three independent experiments. Data are shown as means ± SD. **P < 0.01. (G) RDUR expression was examined by qRT-PCR in indicated cells infected with influenza viruses (PR8 and CA04), Sendai virus (SeV), Muscovy duck reovirus (MDRV), or herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Plotted are the average results from three independent experiments. Data are shown as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.