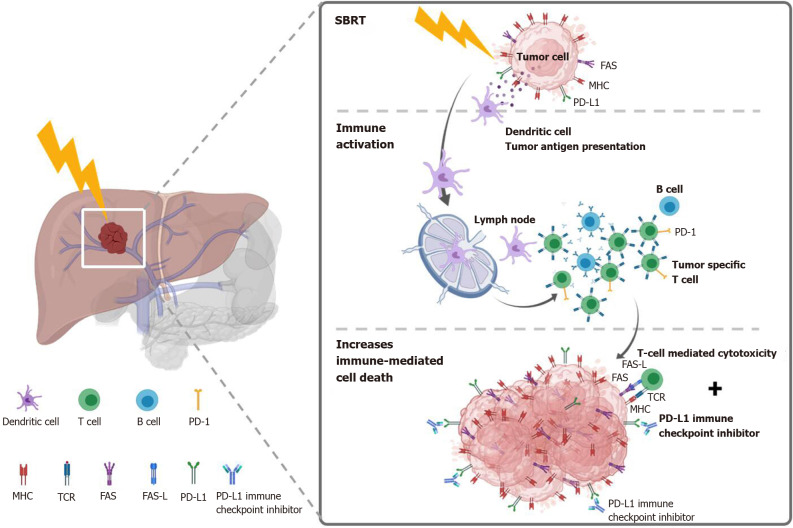
Figure 5.
Potential mechanism of stereotactic body radiation therapy combined with systemic therapy to induce the systemic therapy augmented by radiotherapy effect (also known as immunotherapy and stereotactic ablative radiotherapy) for liver tumors. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) induces antigen release and immunogenic cell death, activation of several transcription factors and signal pathways, as well as dendritic cell antigen presentation and maturation, resulting in proliferation of tumor-specific T cells and immune-mediated cytotoxicity. SBRT combined with Immune-checkpoint inhibitors augmented the tumoricidal effect by upregulates major histocompatibility complex and FAS on tumor cells, increasing susceptibility to T-cell-mediated cell death. MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor; FAS-L: FAS ligand.