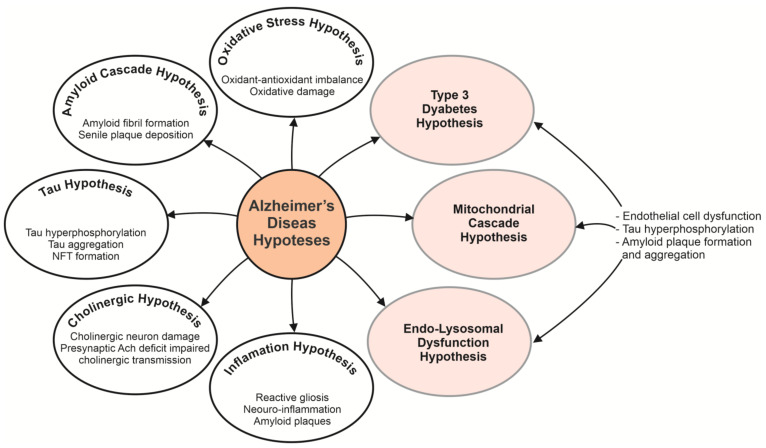
Figure 1.
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease that involves a multitude of factors. Given the complexity of the human brain, the lack of effective research tools and reasonable animal models, the detailed pathophysiology of the disease remains unclear. Based on multifaceted nature of AD, there have been proposed various hypotheses, including Aβ aggregation, cholinergic dysfunction, tau aggregation, oxidative stress, inflammation, etc. Challenges and future prospects include extensive testing of new hypotheses such as endo-lysosomal, mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunctions to attack the disease from different angles for the effective development of an early diagnosis and successful drugs for therapies. NTF, neurofibrillary tangle; Ach, acetylcholine.