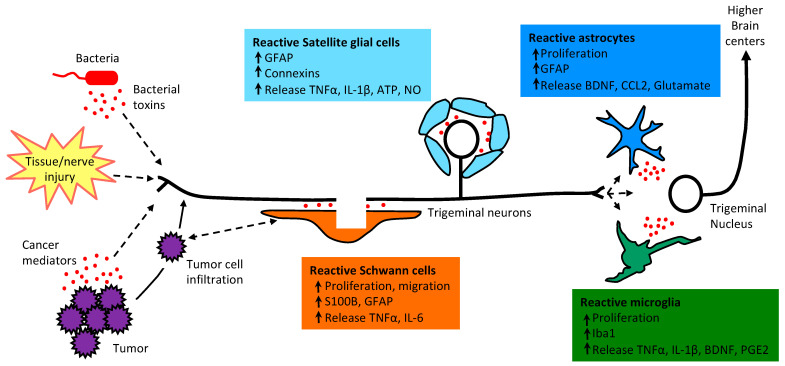
Figure 1.
Functional alterations of glial cells, including Schwann cells, SGCs, astrocytes and microglia in response to rofacial tumors, bacterial toxins, dental pulp injury or tissue/nerve injury. Peripheral injury/inflammation induces an increase in glial cell proliferation and hypertrophy, changes in glial activation markers, and the release of pronociceptive mediators that can contribute to neuronal sensitization and pain. TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL: interlukin; NO: nitrogen oxide; BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor; CCL2: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; PGE2: prostaglandin E2.