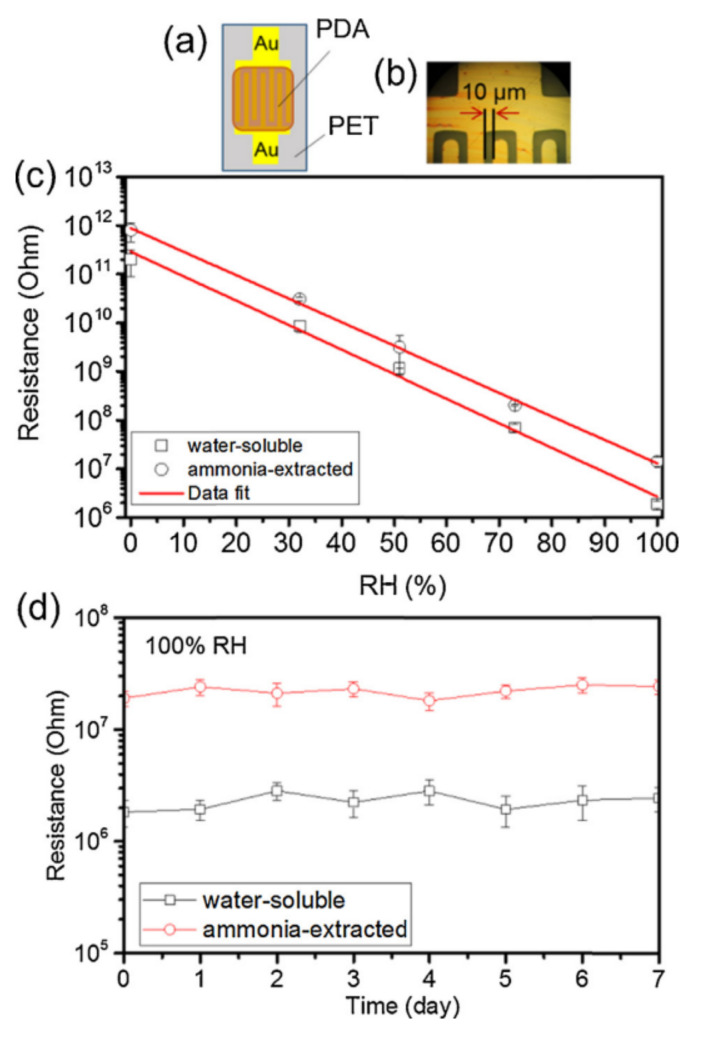
Figure 15.
(a) A schematic structure of the humidity sensing device that Wu et al. fabricated from a polydopamine (PDA) melanin. (b) Shows an optical image of the device. (c) The resistance vs. relative humidity is plotted for two different variations of melanin films, one based upon a water-soluble polymer and the other based upon an ammonia extracted procedure. As can be seen, there is an exponential dependence on the resistance with humidity, making the device sensitive to moisture content. (d) An example of the resistance measured over days, indicating a stable device. This figure was published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 224, T.F. Wu, J.D. Hong, Synthesis of water-soluble dopamine–melanin for ultrasensitive and ultrafast humidity sensor, 178–184, Copyright Elsevier 2016 [145].