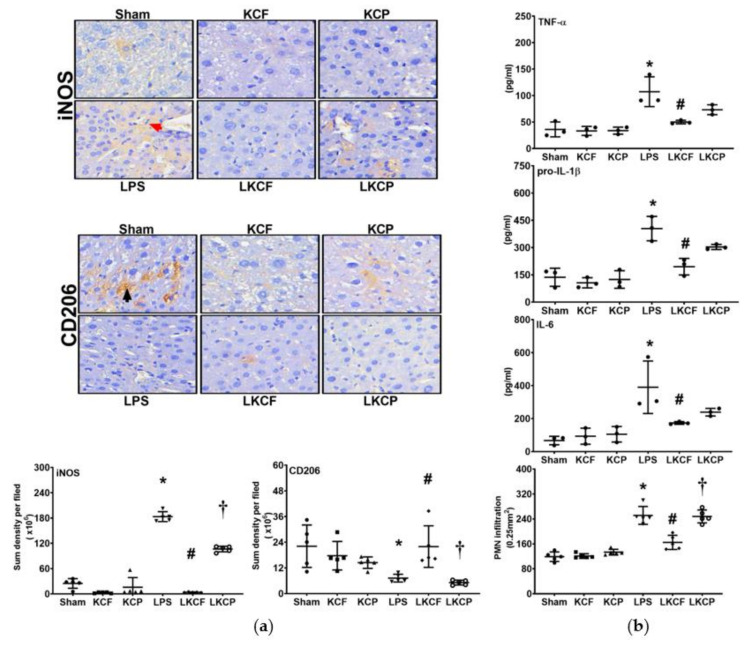
Figure 5.
Liver inflammation status. (a) Characteristic microscopic images (200×) of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, as marked by the red arrow; the M1 phase polarization marker) and CD206 (as marked by the black arrow; the M2 phase polarization marker) in liver tissues obtained by performing immunohistochemistry analysis; findings are presented with the respective quantitative sum intensity of iNOS and CD206. (b) Concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β), and interleukin (IL-6) in liver tissues, as determined using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) infiltration level in liver tissues. Sham: the normal saline (NS) group. KCF: the NS with KCF18 peptide group. KCP: the NS with control peptide (CP) group. LPS: the lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 15 mg/kg) group. LKCF: the LPS with KCF18 peptide group. LKCP: the LPS with CP group. All data were measured 24 h after NS or LPS administration. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Data regarding iNOS, C206, TNF-α, pro-IL-1β, IL-6, and PMN infiltration were derived from 5, 5, 3, 3, 3, and 5 mice from each group, respectively. * p < 0.05, LPS group comparing to Sham group. # p < 0.05, LKCF group comparing to LPS group. † p < 0.05, LKCP group comparing to LKCF group.