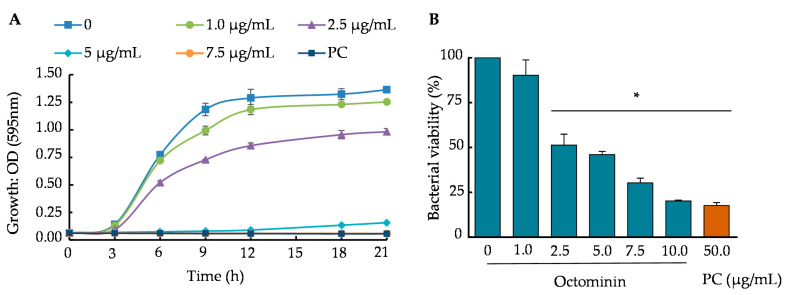
Figure 1.
Time-kill kinetic assay and bacterial viability of A. baumannii upon treatment with Octominin. (A) The time-kill kinetics of A. baumannii treated with Octominin (1.0, 2.5, 5.0, and 7.5 µg/mL) were assessed at every 3 h intervals by measuring the optical density at 595 nm (OD595). Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and 50 µg/mL chloramphenicol were used as the negative and positive controls, respectively. The bars indicate the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). (B) A. baumannii viability upon Octominin treatment. A. baumannii was treated with Octominin at increasing concentrations (0–10 µg/mL) and positive-control chloramphenicol. The samples were incubated for 24 h. Later, a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was performed, and the OD595 was measured. * p < 0.05 compared to the control (0) group. The error bars indicate the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). PC = Positive control (chloramphenicol).