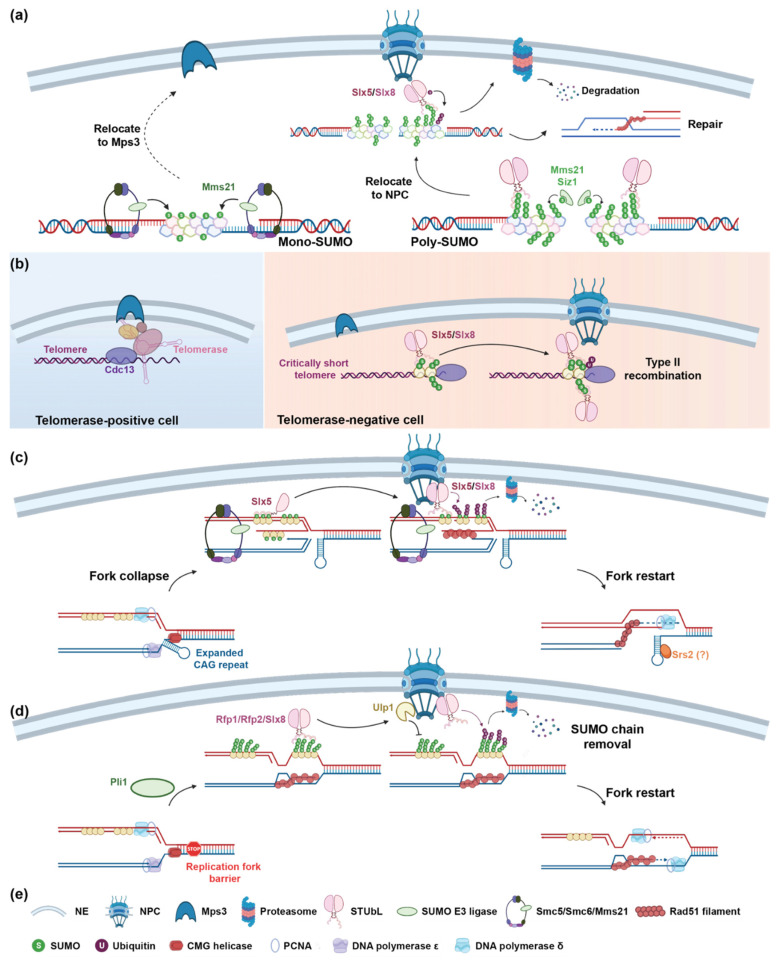
Figure 2.
Relocalization of damaged DNA to the nuclear periphery by STUbLs. (a) Relocalization of irreparable DSBs to the nuclear periphery in S. cerevisiae. Irreparable DSBs that are mono-SUMOylated are relocated to Mps3, whereas DSBs that are poly-SUMOylated are relocated to the NPC in an Slx5/Slx8-dependent manner. Once DSBs are at the NPC, Slx5/Slx8 promotes the degradation of proteins blocking late HR steps, enabling the loading of Rad51 and subsequent repair [219,220,221]. (b) Relocalization of eroded telomeres to the nuclear periphery in S. cerevisiae. In telomerase-positive cells (left), telomeres are associated with NE via the interaction between telomerase and Mps3. In the absence of telomerase, Slx5/Slx8 recognizes SUMOylated proteins that bind to critically short telomeres and relocates them to NPC, at which type II recombination occurs to extend telomere lengths [222,223,224]. (c) Relocalization of collapsed forks to the NPCs in S. cerevisiae. Replication forks are prone to collapse at the expanded CAG repeats. Collapsed forks are processed and bound by RPA, Rad52, and Rad59, which are mono-SUMOylated by Smc5/Smc6 and Mms21. Collapsed forks relocate exclusively to the NPCs in an STUbL-dependent manner. Slx5/Slx8 also facilitates the degradation of Rad52 at the NPCs, allowing the association of Rad51 and subsequent fork restart, potentially with the assistance of Srs2 helicase [97,225]. (d) Relocalization of arrested forks to the nuclear periphery in S. pombe. Arrested forks caused by replication fork barriers are poly-SUMOylated by Pli1 SUMO E3 ligase. Rad51 loading and activity are required before relocalization by Rfp1/Rfp2/Slx8. At the NPC, both Ulp1 SUMO-specific peptidase and STUbL-proteasome can remove poly-SUMO chains, which are inhibitory to fork restart [172]. (e) Key to proteins and compartments shown in (a–d). Figures were created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: STUbL, SUMO-targeted E3 ubiquitin ligase; Mps3, mono polar spindle 3; DSB, DNA double-strand break; NPC, nuclear pore complex; HR, homologous recombination; NE, nuclear envelope; RPA, replication protein A; Smc5/Smc6, structural maintenance of chromosome protein 5/6; Mms21, methyl methanesulfonate sensitivity 21; CMG, Cdc45-Mcm2-7-GINS; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; Siz1, SAP and mIZ-finger domain 1; Srs2, suppressor of Rad6 2.