FIGURE 7.
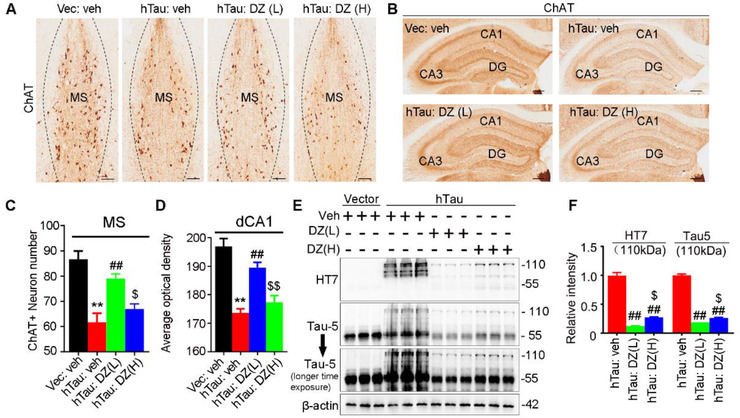
Low‐dose donepezil more prominently rescues MS‐hTau‐induced cholinergic loss with removal of tau proteins. (A–D) Both high‐ and low‐dose donepezil restored ChAT staining, and the effect of low dose was more prominent than high dose in MS (A and C, scale bar = 100 μm) and hippocampus (B and D, scale bar = 100 μm) measured by ChAT immunohistochemistry staining. One‐way ANOVA group, F(3, 32) = 16.08, p < .01 (**p < .01 vs. Vec:veh, ##p < .01 vs. hTau:veh, $p < .05 vs. hTau:DZ(L)) (C) or F(3, 52) = 25.52, p < .01 (**p < .01 vs. Vec:veh, ##p < .01 vs. hTau:veh, $$p < .01 vs. hTau:DZ(L)) (D). (E and F) Low‐dose donepezil more significantly decreased human tau proteins (HT7 and Tau‐5 at ∼110 kDa band) than high dose in MShTau mice measured by Western blotting. One‐way ANOVA group, F(2, 6) = 254.9, p < .01 (HT7); F(2, 6) = 802.1, p < .01 (Tau‐5). #p < .05, ##p < .01 versus hTauMS:veh, $p < .05. HT7 specifically reacts with the exogenously expressed hTau, and Tau‐5 reacts with total tau proteins. Data are presented as mean ± SEM
