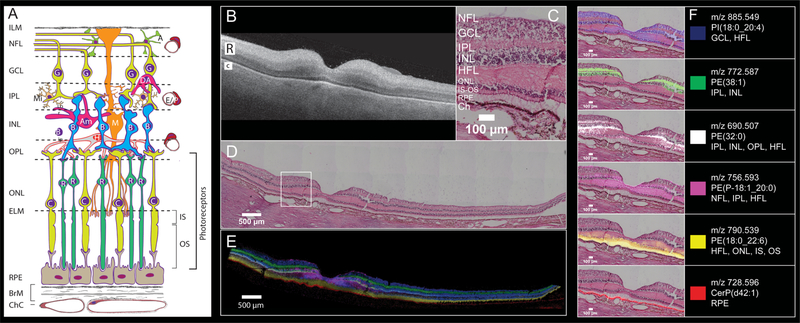
Figure 2.
Six MALDI IMS signals with distinct laminar localizations in human macula from an 83-year-old female donor. (A) Schematic diagram of retina, Bruch’s membrane, and choriocapillaris, indicating cell types in their characteristic layers. The outer nuclear layer (ONL) contains cell bodies of cones (C) and rods (R) and their inner fibers, all interleaved with Müller glia (M). Photoreceptor inner segments (IS) contain many mitochondria. Photoreceptor outer segments (OS) contain phototransduction-related proteins in membrane disks. The RPE apical processes are specialized for metabolic exchange with photoreceptors and retinoid processing. Layers: ILM, inner limiting membrane; NFL nerve fiber layer, GCL ganglion cell layer, IPL inner plexiform layer, INL inner nuclear layer, HFL Henle fiber layer, ELM, external limiting membrane; RPE retinal pigment epithelium, ChC, choriocapillaris; BrM, Bruch’s membrane; cell types, A, astrocyte; Am, amacrine; B, bipolar; E, endothelium; G, ganglion cell; H, horizontal cell; P, pericyte. (B) OCT B-scan of a donor eye macula prior to sample preparation, R and C indicating retina and choroid, respectively. The retina is at the top, the choroid (vasculature) is on the bottom, and the hyperreflective interface is the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) layer. (C) Zoomed image of tissue section stained with H&E to indicate cell layers at the level shown in (A). NFL nerve fiber layer, GCL ganglion cell layer, IPL inner plexiform layer, INL inner nuclear layer, HFL Henle fiber layer, ONL outer nuclear layer, IS-OS photoreceptor inner and outer segments, RPE retinal pigment epithelium, Ch choroid. (D) Panoramic H&E stained tissue post-IMS data acquisition showing macula and extended stretch of temporal peripheral retina. (E) Overlay of MALDI IMS images of selected lipid signals localizing to distinct retinal layers and RPE as indicated. Colors defined in panel F. (F) Individual ion signals overlaid on top of H&E stained tissue image.