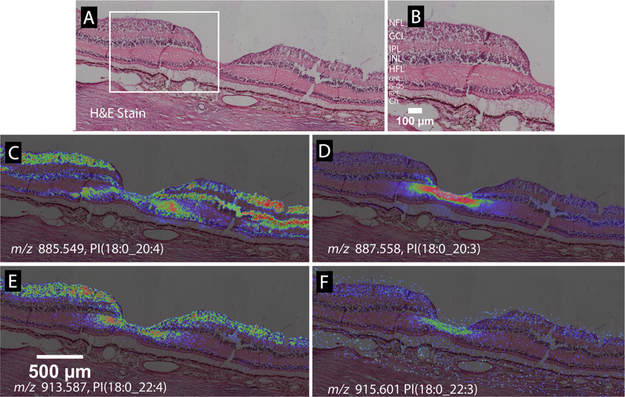
Figure 5.
Lipid species varying in only one double bond can exhibit different MALDI IMS distributions. (A) H&E stained tissue image of a normal macula, with the foveal pit in the center. (B) Zoomed view of panel A showing retinal layers. NFL, nerve fiber layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; HFL, Henle fiber layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PR/IS, photoreceptor inner segments; PR/OS, photoreceptor outer segments; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ChC, choriocapillaris. (C) m/z 885.5499, PI(18:0_20:4) distributes in the foveal center, GCL, INL, and HFL. (D) m/z 887.558, PI(18:0_20:3), with one double bond less than the species in panel C, localizes to the HFL of the foveal center and the inner INL. (E) m/z 913.587, PI(18:0_22:4) localizes to the foveal center, GCL, INL, and HFL, like the species in panel A, but with a lesser lateral extent of INL. (F) m/z 915.601, PI(18:0_22:3), with one double bond less than the species in panel E, localizes to the HFL of the foveal center.