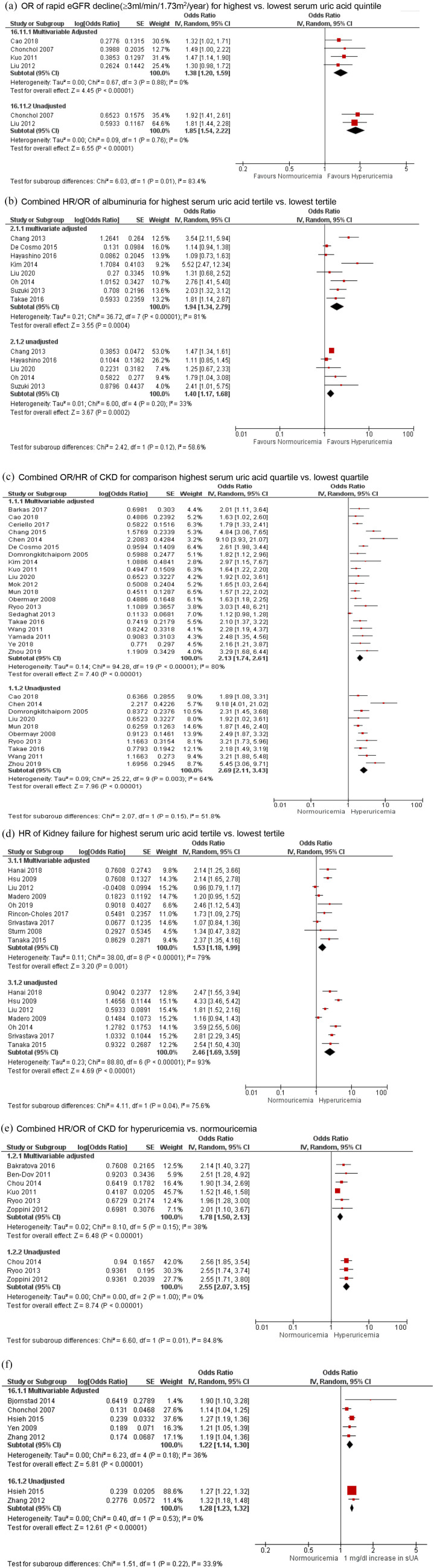
Figure 2.
Hyperuricemia and multivariable-adjusted and unadjusted risk of chronic kidney disease, end stage kidney disease, albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in longitudinal analysis. (a) OR of rapid eGFR decline (⩾3 ml/min/per 1.73 m2/year) for highest versus lowest serum uric acid quintile. (b) Combined HR/OR of albuminuria for highest serum uric acid tertile versus lowest tertile. (c) Combined OR/HR of CKD for comparison of highest serum uric acid quartile versus lowest quartile. (d) HR of kidney failure for highest serum uric acid tertile versus lowest tertile. (e) Combined HR/OR of CKD for hyperuricemia versus normouricemia. (f) Combined HR/OR of rapid eGFR decline (⩾3 ml/min/per 1.73 m2/year) for every 1 mg/dl increase in serum urate.
CI, confidence interval; CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; IV, inverse variance; OR, odds ratio; sUA, serum urate