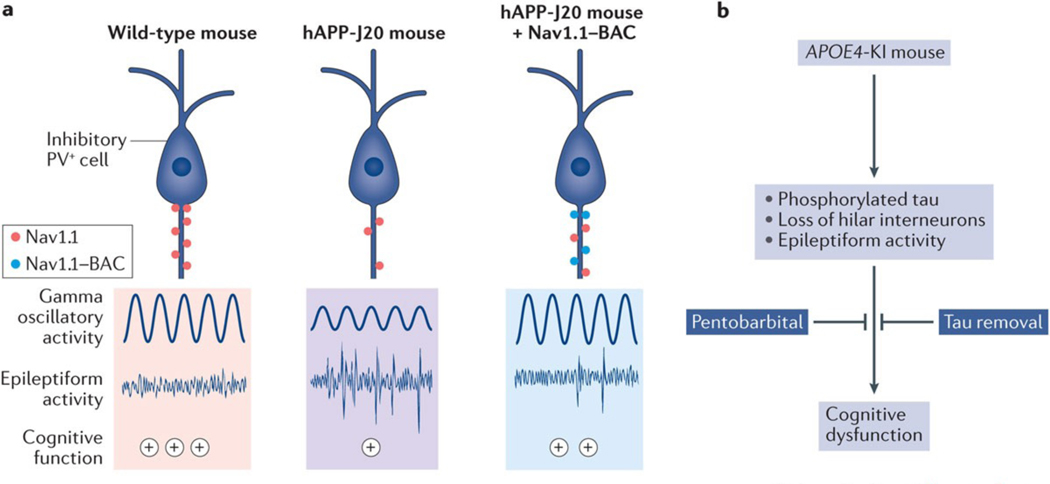
Figure 6 |. Targeting interneurons to improve Alzheimer disease-related network dysfunction.
a | In hAPP-J20 mice (middle panel), reduced levels of the voltage-gated sodium chanel subunit Nav1.1 in parvalbumin-positive (PV+) cells were associated with reduced gamma power, epileptiform activity and cognitive impairment (the level of cognitive performance is denoted by the plus symbols). Restoring Nav1.1 levels in PV+ cells with an Nav1.1-BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) transgene (right panel) reduced all of these deficits. b | APOE4-KI mice have increased neuronal levels of phosphorylated tau, age-dependent loss of somatostatin-positive interneurons in the hilus of the dentate gyrus, and seizures. Memory deficits in these mice were reduced by pentobarbital treatment221, tau removal221 and transplantation of interneuron precursor cells160. Part a is adapted with permission from REF. 172, Cell Press/Elsevier.