Figure 3. . Stem cells and oncolytic virotherapy.
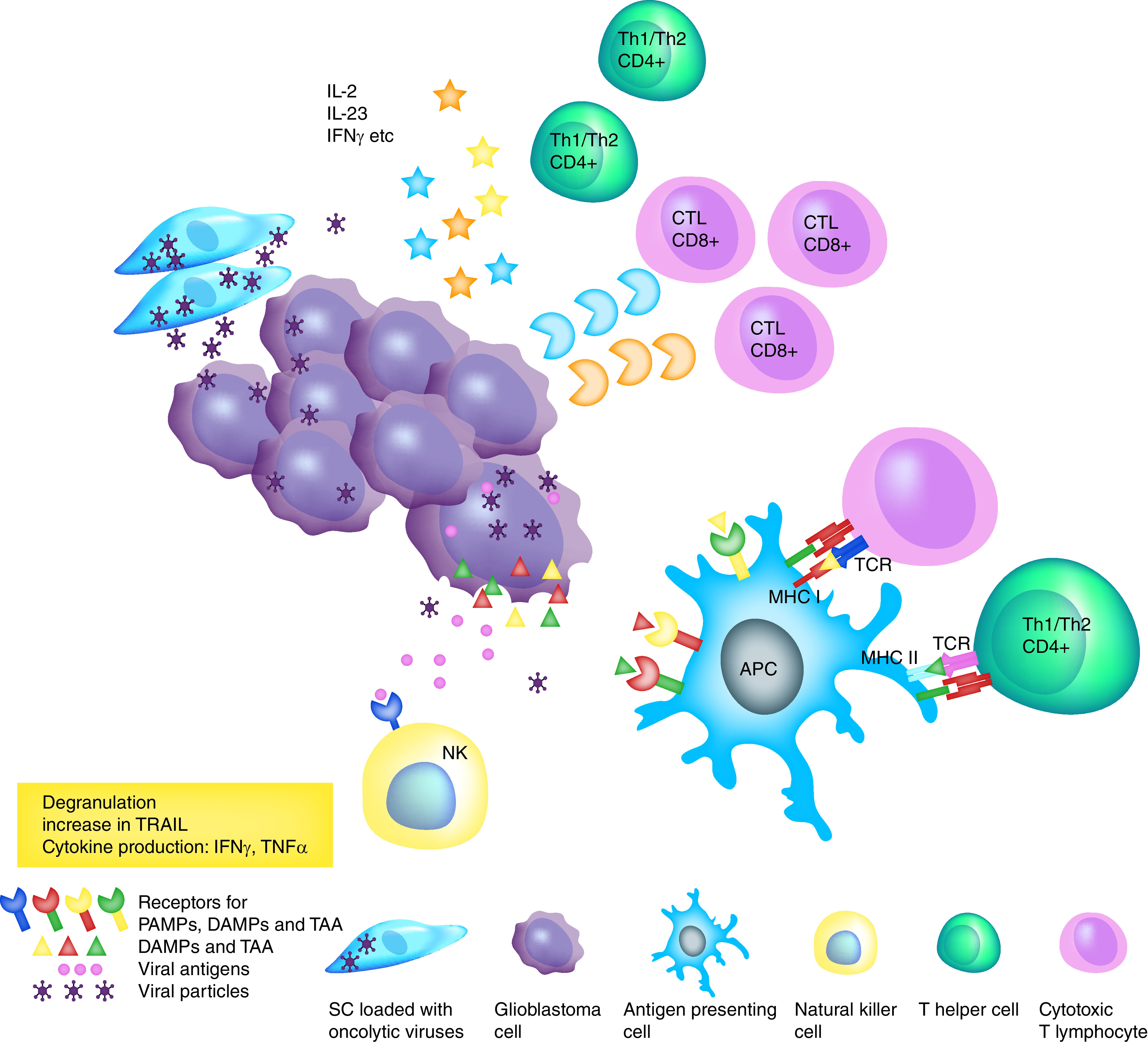
Intratumoral delivery of oncolytic viruses by SCs results in virus-induced glioma tumor cell death and also in immunogenic cell death through activation of the innate and adaptive antitumor immune responses. Dying cells release viral antigens (PAMPs), DAMPs and TAAs. These antigens activate NK cells that induce direct tumor cell killing through production of granzyme and perforin, and also induce apoptosis through the release of TRAIL, TNF-α and IFN-γ. DAMPs and TAA activate antigen-presenting cells that travel to the draining lymph nodes, where they cross-present antigens to naive T lymphocytes and activate them. Activated T helper and cytotoxic T lymphocytes migrate into the tumor and release cytokines, perforin and granzyme that amplify the cytotoxic effect.
APC: Antigen presenting cell; DAMP: Damage-associated molecular pattern; NK: Natural killer; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular pattern; SC: Stem cell; TAA: Tumor-associated antigen; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
