Figure 1.
The parental genomes cluster with nucleoli at the pronuclear interface in live human zygotes
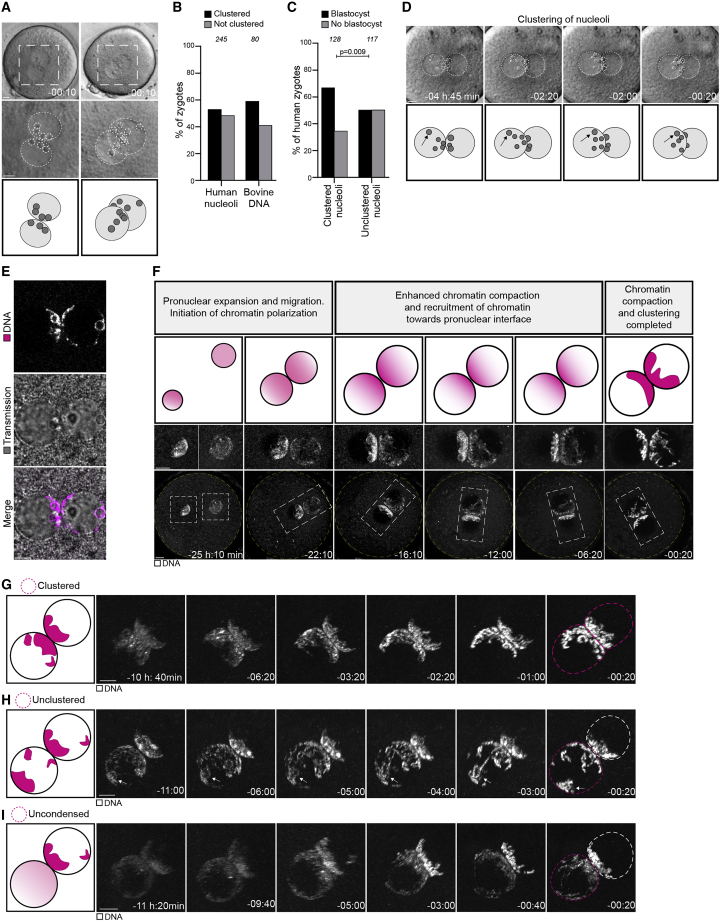
(A) Top: representative stills from time-lapse movies of a human zygote that develops (left) or fails to develop (right) into a blastocyst. Zygotes have clustered (left) or unclustered (right) nucleoli at the pronuclear interface. Middle: magnifications of the regions outlined above. Dashed lines indicate nucleoli and pronuclei. Bottom: schematics of the pronuclei and nucleolar distribution. Time, h:min, 00:00 is NEBD.
(B) Human and bovine zygotes with clustered or unclustered nucleoli (human) or DNA (bovine).
(C) Zygotes with clustered or unclustered nucleoli that develop into blastocyst or abnormally.
(D) Top: representative stills from a time-lapse movie of a zygote. Dashed lines indicate nucleoli and pronuclear outlines. Bottom: schematics of the pronuclei and nucleolar distribution. Arrows indicate a nucleolus that moves toward the pronuclear interface.
(E) Representative stills from time-lapse movies of zygotes. Magenta, DNA (5-580CP-Hoechst). Gray, transmission.
(F) Top: schematics of chromatin organization during pronuclear migration in zygotes. Bottom: representative stills from time-lapse movies of pronuclear migration in zygotes. White, DNA (5-580CP-Hoechst). Outlined regions magnified above. Yellow dashed lines indicate the cell surface. Time, h:min, 00:00 is NEBD. Z projections of 27 (−25:10), 12 (−22:10 and −16:10), 15 (−12:00), and 11 (−06:20 and −00:20) sections every 1.00 μm. Images generated with Imaris 3D view.
(G–I) Schematics (left) and representative stills from time-lapse movies (right) of pronuclei in zygotes before NEBD classified as clustered (G), unclustered (H), and uncondensed (I). White, DNA (5-580CP-Hoechst). Magenta dashed line marks the pronucleus determining the specific category. The arrows in (H) mark chromatin around an unclustered nucleolus. Time, h:min, 00:00 is NEBD. Images generated using Imaris 3D view.
The number of analyzed zygotes (B and C) is specified in italics. p values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. Scale bars, 10 μm.