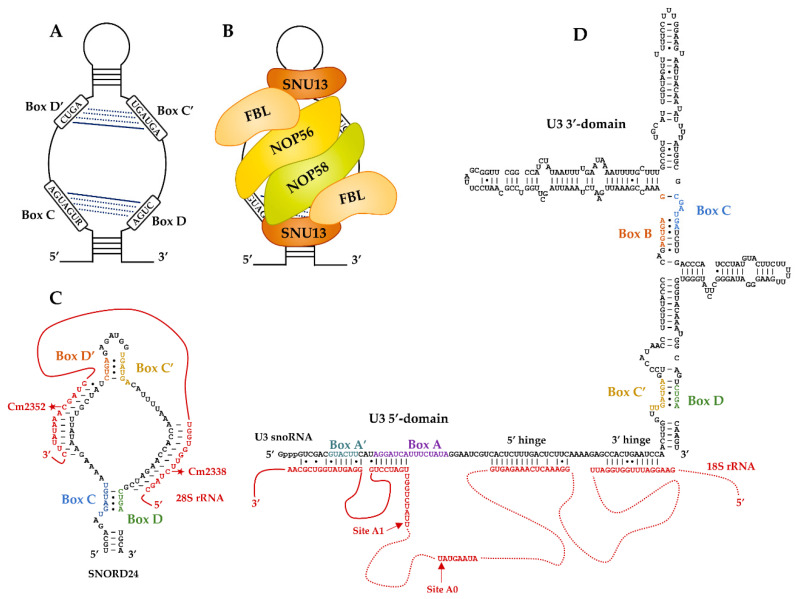
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of guide box C/D small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (C/D snoRNPs) and their target RNAs. (A) Box C/D small nucleolar RNAs (C/D snoRNAs) contain conserved sequences called C/D and C′/D′ boxes that fold into a kink-turn (K-turn) containing Watson–Crick pairings (solid blue lines) and non-canonical pairings U:U, G:A, and A:G (dotted blue lines). (B) Conventional C/D box snoRNPs associate a C/D snoRNA with the core proteins Nop1p/Fibrillarin (FBL), Nop58p/NOP58, Nop56p/NOP56 and Snu13p/SNU13 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Human, respectively. FBL is the methyltranferase that catalyzes the 2′-O-methylation of target RNAs. (C) Schematic representation of the bidimensional human SNORD24 structure (adapted from [50]). This snoRNA guides the 2′-O-methylation of 28S rRNA at positions C2338 and C2352. Classically, the methylated nucleotide (red star) hybridizes with the nucleotide located at the fifth position upstream of the D and D′ box sequences. (D) Schematic representation of the bidimensional U3 snoRNA structure and its association with pre-18S rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (adapted from [61,62]). U3 contains two C/D-like motifs called C′/D and B/C boxes that fold into a K-turn recognized by the Snu13p core protein [14]. In addition, the B/C motif recruits Rrp9p (U3-55K in humans) that is essential for 18S rRNA processing. The A/A′ motifs and the 5′/3′ hinges, located in the 5′ terminal domain of U3, hybridize with the 18S rRNA (solid red lines) and the 5′ ETS (external transcribed spacer, dotted red lines) of the 35S pre-rRNA, respectively. The base-pairing is located near the A0 and A1 pre-rRNA cleavage sites and is essential for the processing of 18S rRNA.