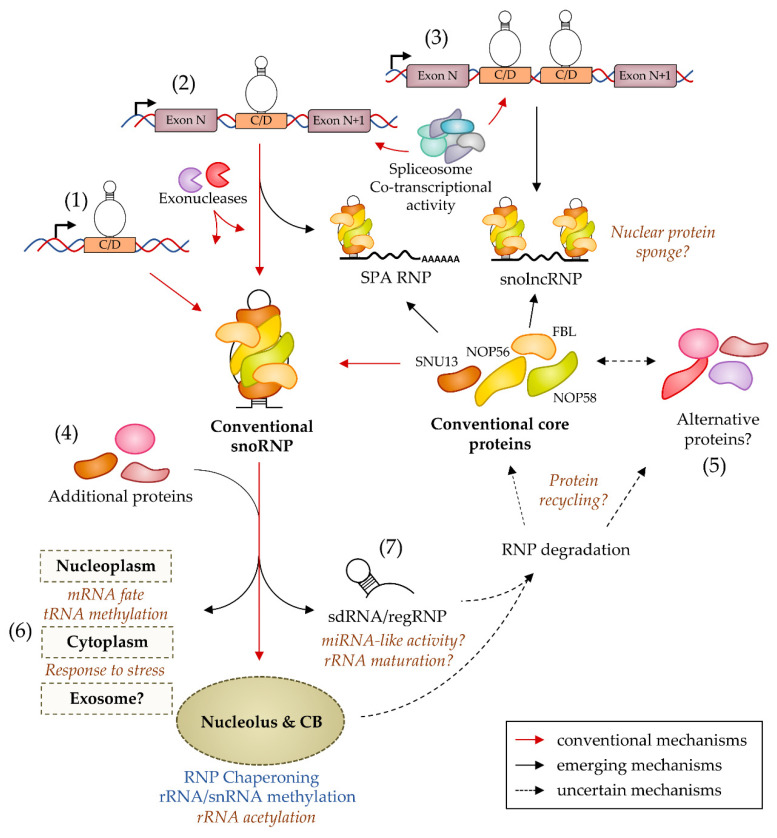
Figure 3.
The emerging diversity of C/D box snoRNA processing and of C/D snoRNP biogenesis and function. Precursor C/D box snoRNAs are produced by both independent (1) and intronic (2 and 3) genes, then processed by the combined action of intron lariat debranching in the case of intronic snoRNAs and exonucleotidic activities acting at both the 5′ and 3′ ends. Co-transcriptional recruitment of snoRNP core proteins on the snoRNA allows the correct processing and biogenesis of the C/D snoRNP. Then, the particle reaches the Cajal body (CB) and the nucleolus to perform activities on snRNAs and rRNAs (in blue). In addition to these conventional mechanisms, C/D snoRNPs perform new activities (in gold italics) linked to the formation of lncRNAs flanked by snoRNA sequences at one or both ends generated from partially-processed, snoRNA-hosting introns (3), to the recruitment of additional proteins conferring new properties and/or enzymatic activities (4) or to the exchange of conventional core proteins by alternative proteins (5), to the trafficking to new subcellular locations (6), and to the generation of snoRNA-derived fragments (sdRNAs) or regulatory ribonucleoproteins (regRNPs; 7).