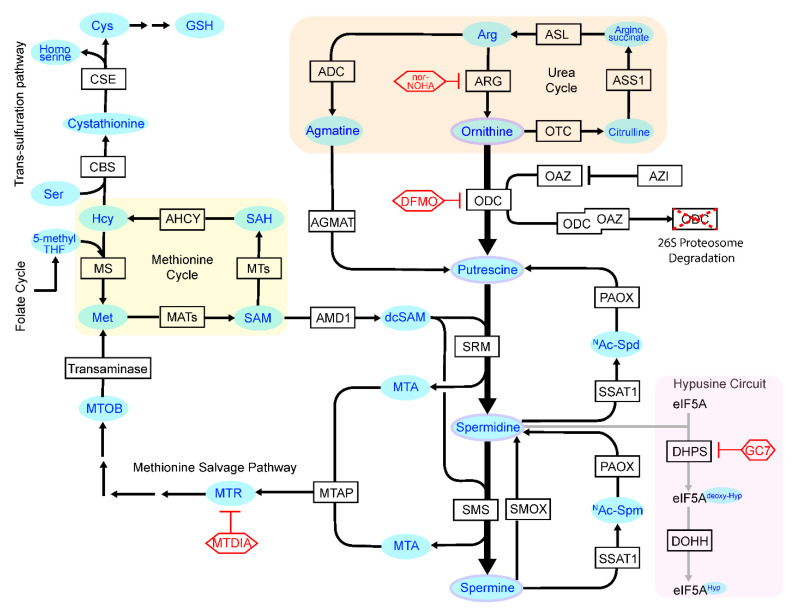
Figure 1.
Polyamine metabolism and interacting pathways. Enzymes that control central polyamine biosynthesis and catabolism are shown, as well as the metabolic circuits that feed into the control of polyamine homeostasis. Light blue, substrates and products; red, inhibitors of key enzymes. ADC, Arginine decarboxylase; AHCY, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; AMD1, Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase-1; AGMAT, Agmatinase; Arg, Arginine; ARG, Arginase; ASL, Arginosuccinate lyase; ASS1, Arginosuccinate synthase-1; AZIN1, Antizyme inhibitor-1; Ac-Spd, N1-acetylated Spd; Ac-Spm: N1-acetylated Spm; CBS, Cystathione β-synthase; CSE, Cystathionine γ-lyase; Cys, Cysteine; DFMO, Difluoromethylornithine; DHPS, Deoxyhypusine synthase; DOHH, Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase; eIF5A, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A; GC7, N1-guanyl-1, 7-diamine-heptane; GSH, Glutathione; HS, Homocysteine; Hyp, Hypusine; MATs, Methionine adenosyltransferases -1, -2A and -2B; Met, Methionine; MTA, 5′methylthioadenosine; MTAP, MTA phosphorylase; MTDIA, Methylthio-DaDMe-Immucillin-A; MTOB, 4-Methylthio-2-oxobutanoic acid; MTR: 5′ methylthioribose; MTs, Methyltransferase; MS, Methionine synthase; nor-NOHA, Nω-hydroxy-nor-arginine; ODC, Ornithine decarboxylase; OAZs, ODC antizyme-1, -2 and -3; OTC, Ornithine transcarbamylase; PAOX, Polyamine oxidase; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAHH. SAH hydrolase; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; Ser, Serine; SSAT1, SPD/SPM acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1); SMOX, Spermine oxidase; SMS, Spm synthase; SRS, Spd synthase.