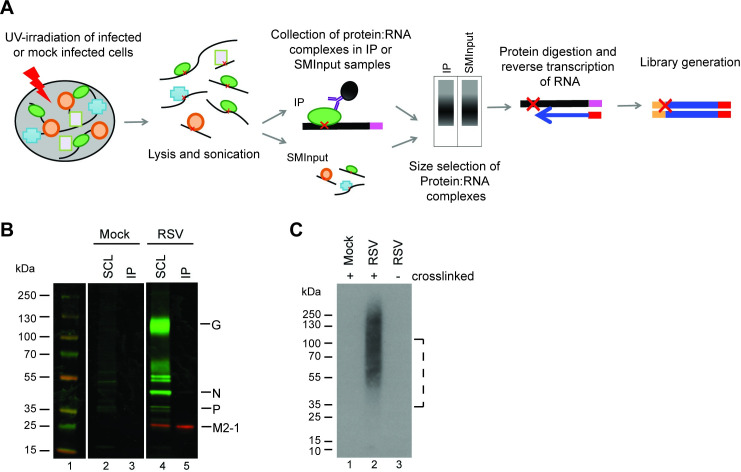
Fig 1. Experimental design to identify RNA bound by M2-1.
(A) Overview of seCLIP-seq procedure. RSV infected cells were subjected to UV-irradiation to crosslink RNA and protein complexes. Cells were lysed and RNA sheared by sonication. A subsample of lysate was removed for the SMInput control while the remaining was subjected to immunoprecipitation using an M2-1 specific antibody. Protein: RNA complexes were separated by size by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. RNA was released from the membrane by proteinase digestion, reversed transcribed to the site of the protein:RNA crosslink (indicated with a red X), and used to generated a library, which was analyzed by sequencing. (B) Western blot analysis of RSV proteins immunoprecipitated from infected cells by the anti-M2-1 22k4 antibody following UV-cross linking. Soluble cell lysates (SCL) and immunoprecipitated complexes (IP) were analyzed by Western blotting using a polyclonal anti-RSV antibody (green) and an M2-1 specific antibody (red). (C) Visualization of RNA immunoprecipitated in complex with M2-1. Cells were mock infected or infected with RSV A2 and subjected to UV light cross-linking (40 mJ/cm2) or not, as indicated. Cell lysates were treated as described above, except that immunoprecipitated RNA was radio-labeled prior to SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and analyzed by autoradiography. The dotted line indicates the region that was excised in the subsequent seCLIP-seq analysis (which entailed unlabeled RNA).