Fig. 1.
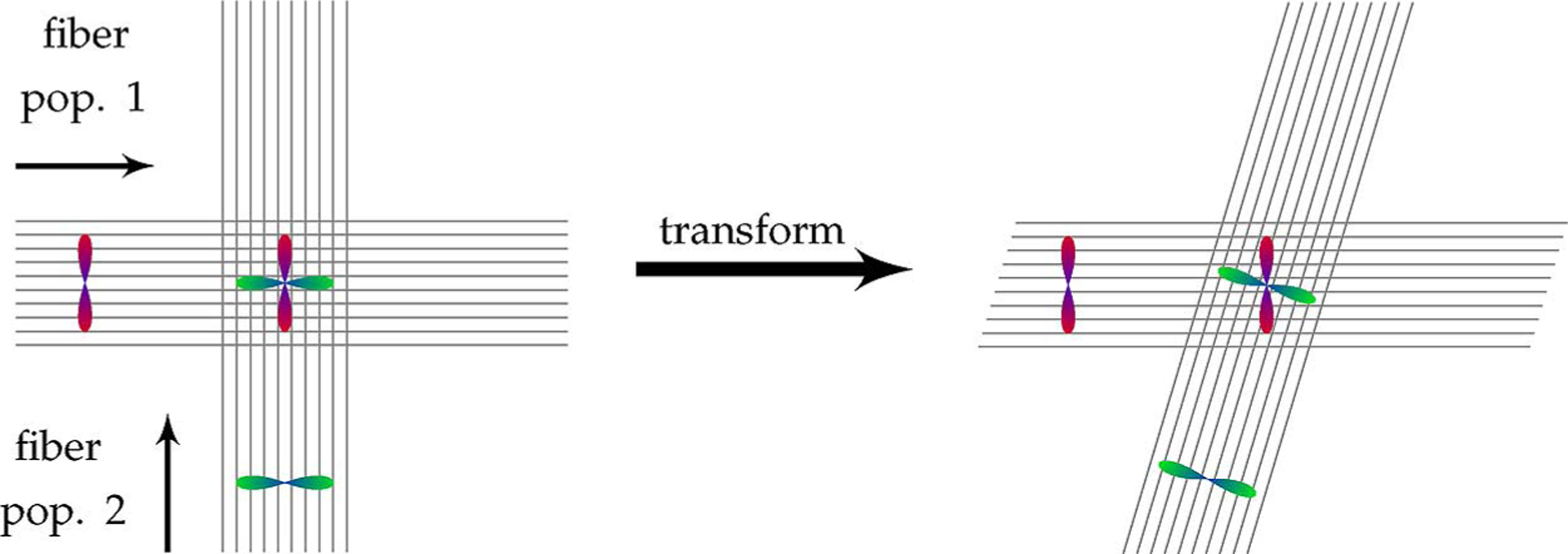
DWI reorientation. Two fiber populations, one horizontal and one vertical, are shown together with their individual diffusion-attenuated signal profiles. When the two fiber populations cross each other, the resulting signal profile is a combination of signals from the individual fiber populations. Since the individual fiber populations transform differently with respect to a local transformation (horizontal shearing in this example), the signal profiles of the individual fibers need to be decoupled, reoriented individually, and then recombined to form a reoriented signal profile.
