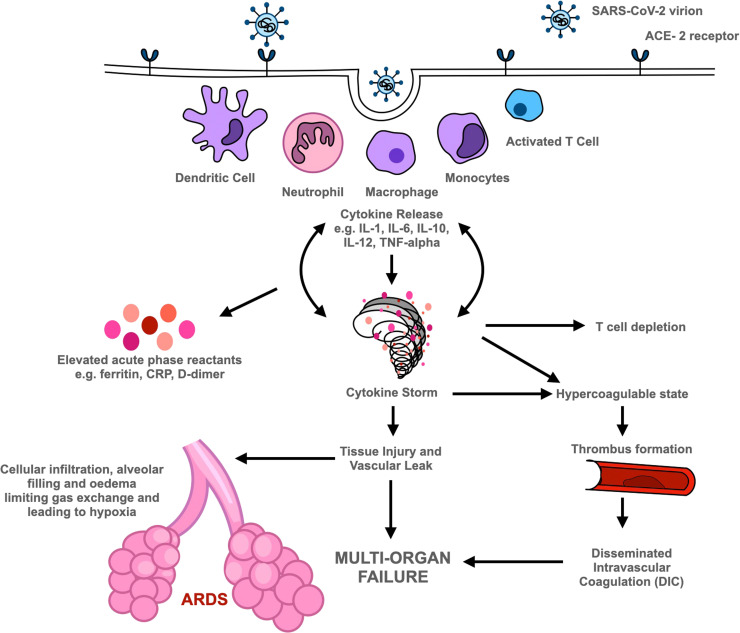
Fig. 2.
Pathogenesis of COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 virion binds to ACE-2 receptor gaining entry into cells. This triggers the innate and adaptive immune responses, with cytokine release and elevated levels of acute phase reactants. Increased cytokine release contributes to T cell depletion and cytokine storm. Cytokine storm has multiple effects including widespread activation of the coagulation cascade contributing to thrombus formation and can further lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation; tissue injury within the lung that can progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); systemically increased vascular permeability and tissue injury that can cause multi-organ failure and subsequent death. Footnote (to appear belowFig. 2): WHO international standards are available for a wide range of substances from NIBSC, https://www.nibsc.org/. These include systemic markers of inflammation (cytokines, chemokines, other biomarkers e.g., C-reactive protein, ferritin etc) for use in assays used in measurement of these analytes. Recently available international standards and other reagents for SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 research include 1stWHO IS for SARS-CoV-2 RNA for nucleic-acid amplification assays and the WHO IS for anti-SARS-COV-2 for serology assays.