Figure 2.
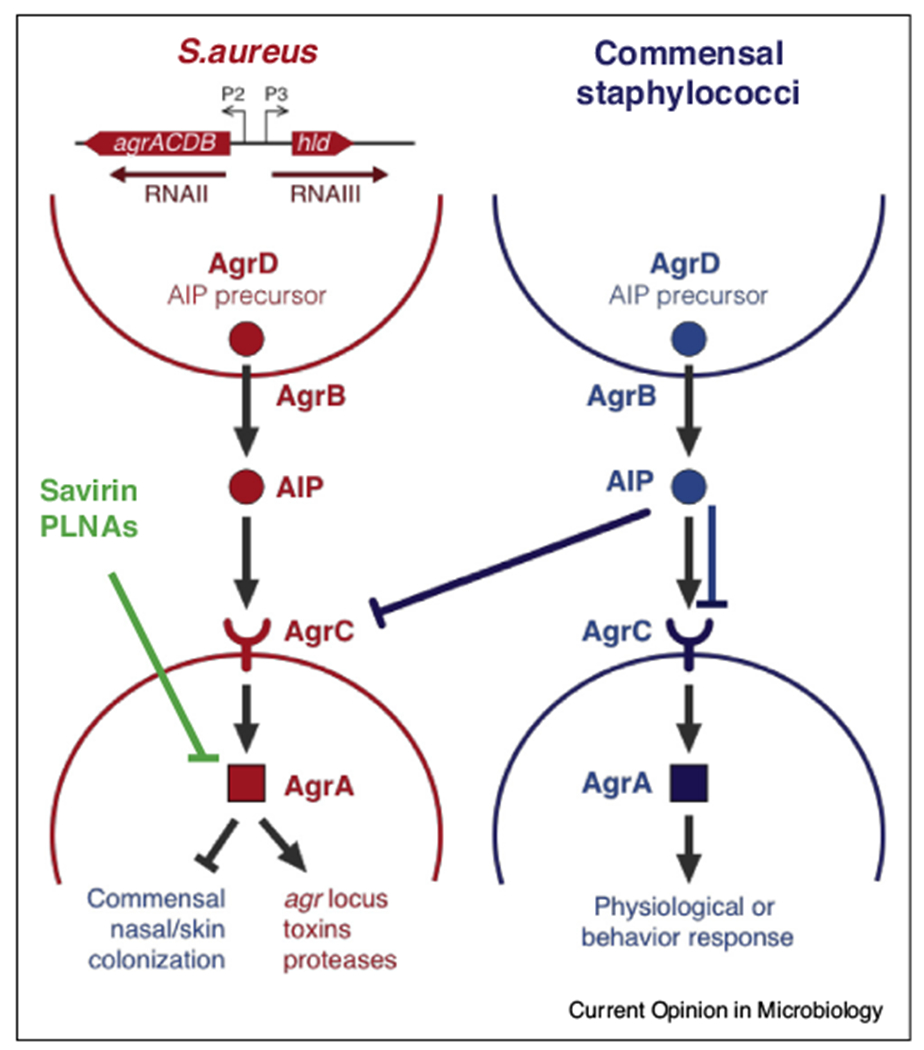
The agr quorum sensing system in S. aureus. The agr locus consists of two divergently encoded operons, agrACDB and RNAIII, which are activated by the transcription factor AgrA. The agrACDB operon encodes AgrD, which is the precursor for the QS signal autoinducing peptide (AIP); AgrB, which is the machinery that processes and secretes AIP; and the AgrAC two-component system comprises the AIP receptor AgrC and its cognate response regulator AgrA. The RNAIII operon consists of the regulatory RNA, RNAIII, and the δ-toxin encoded by hld. AgrA and RNAIII together activate virulence-associated functions such as toxin production, secretion of phenol soluble modulins (PSMs) and protease activity and inhibit the expression of cell surface proteins associated with commensalism. Coagulase negative staphylococcal commensals produce AIPs that inhibit the AgrC receptor in S. aureus, thus attenuating its virulence, they may also inhibit AgrCs from other commensals. Additionally Savirin and PNLAs also inhibit Agr signaling.
